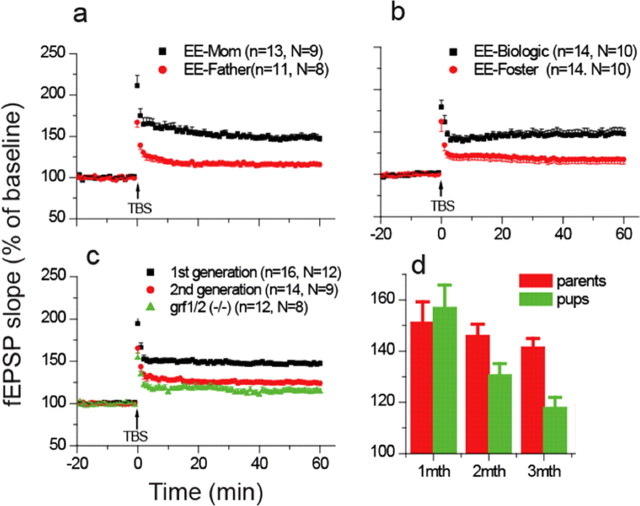
Figure 4.
Mechanism of transmission of EE effects across generations. a, LTP assays on hippocampal slices from 1-month-old offspring of enriched female and unenriched male (black squares) or enriched male and unenriched female (red circles) ras-grf1/grf2 double knock-out mice. b, LTP assays on hippocampal slices from the offspring of enriched ras-grf knock-out mice but raised by unenriched foster mothers (EE-Biologic-black squares) or offspring of unenriched ras-grf knock-out mice raised by enriched foster mothers (EE-Foster-red circles). c, LTP assays on 1-month-old F1-generation offspring (black squares), or F2 second-generation offspring (red circles) of enriched ras-grf knock-out mice. Samples from 1-month-old unenriched ras-grf knock-out mice (green triangles) are also shown for comparison. d, LTP assays were performed on hippocampal slices from enriched ras-grf knock-out mice (red bars) and F1 offspring of enriched ras-grf knock-out mice (green bars) at 1 month of age. Mice were then returned to a conventional environment and assayed at 2 months of age and 3 months of age. Data are the average fold increase in fEPSP slopes from three experiments (Fig. 1C).