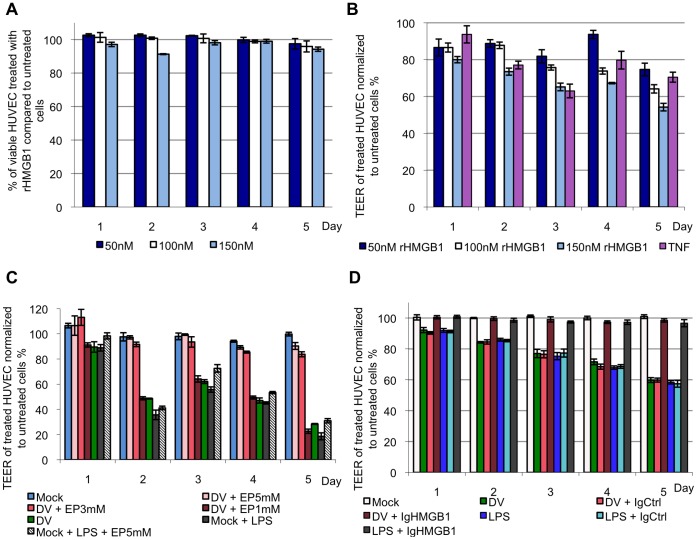
Figure 3. HMGB1 induces vascular leakage in endothelial cells, which can be restored with EP.
A, HUVEC was incubated with 50, 100 or 150 nM of rHMGB1 for 5 days and cell viability assay was performed to assess for cytotoxicity induced by rHMGB1 on HUVEC. The percentage of the viable cells from the rHMGB1 treated groups was calculated in relation to the untreated negative control cells. B, 50, 100 and 150 nM of rHMGB1 was added to the confluent HUVEC monolayer to observe for the presence of vascular leakage (indicated by a lowered TEER value) in the endothelial cells. The TEER values of the rHMGB1-treated monolayer were expressed as percentage to the untreated negative control cells. TNF-α, a known inducer of vascular leakage was added to HUVEC monolayer was used as a positive control. C, cell culture supernatant of K562 mock- or DV-infected and EP-treated was collected 3 d.p.i. and added to HUVEC monolayer for 5 days. The TEER of the HUVEC monolayer was measured and the values of the monolayer treated with mock-infected, DV-infected and EP-treated K562 cell culture supernatants were expressed as percentage to HUVEC treated with K562 cell culture medium RPMI-1640 in the absence of any treatment of viral infection. D, mock- or DV-infected or LPS-treated K562 cell culture supernatant was added to HUVEC monolayer for 5 days with chicken anti-HMGB1 neutralizing antibody (IgHMGB1) or chicken HMGB1 control chicken IgY (IgCtrl). The TEER of the supernatant-treated cells was expressed as percentage to HUVEC treated with control RPMI-1640 cell culture medium.