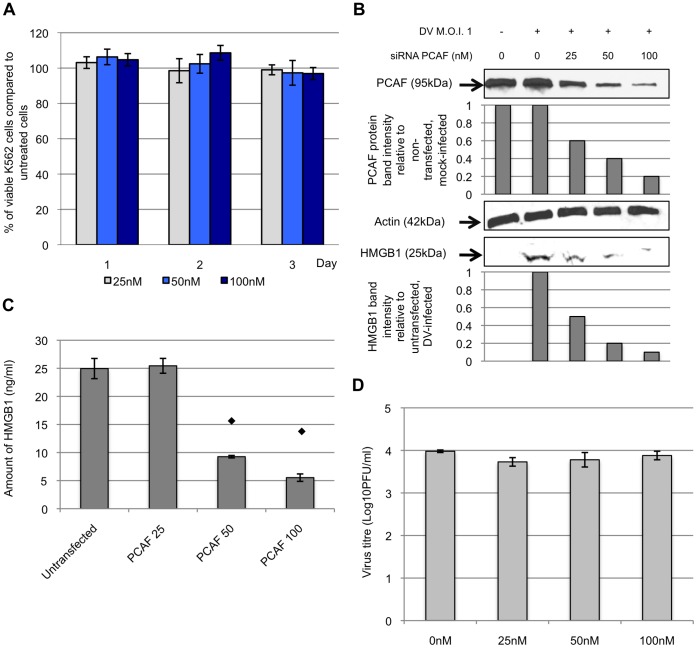
Figure 4. DV mediates HMGB1 release through the involvement of PCAF acetylase complex.
A, K562 cells were transfected with 25, 50 or 100 nM of siRNA for 3 days and cell viability assay was performed to evaluation of the cytotoxicity of siRNA transfection on K562 cells. The percentage of the viable transfected cells was expressed as a percentage to that of the non-transfected cells. B, siRNA (concentration of 25 to 100 nM) targeting against PCAF was used to transfect K562 cells. The transfected K562 cells were subjected to DV infection 48 hours post-transfection. The cell lysates and culture supernatants were harvested at 1 d.p.i. and Western blot analysis was then performed to detect for the presence of PCAF and HMGB1, respectively. The PCAF band intensities of the siRNA transfected K562 cells were calculated in relation to the non-transfected mock-infected cells (assigned to a value of 1). Similarly, the band intensities of HMGB1 of the transfected cell culture supernatants were measured in relation to the band intensity of non-transfected DV-infected cell culture media (assigned to value of 1). Actin was used as a control to ensure equal loading. C, ELISA was performed to quantify the amount of HMGB1 released into the supernatants from siRNA transfected (0, 25, 50 or 100 nM of siRNA) and DV-infected K562 cells. ⧫ denotes p-value <0.05 for T-tests comparing the mean amount of HMGB1 detected in siRNA transfected K562 cell culture supernatants to that of the non-siRNA transfected K562 cells. D, K562 cells were transfected with 0, 25, 50 or 100 nM of siRNA for 48 hours before infected with DV. The supernatants were harvested at 1 d.p.i. and plaque assay was performed to quantify the viral yield.