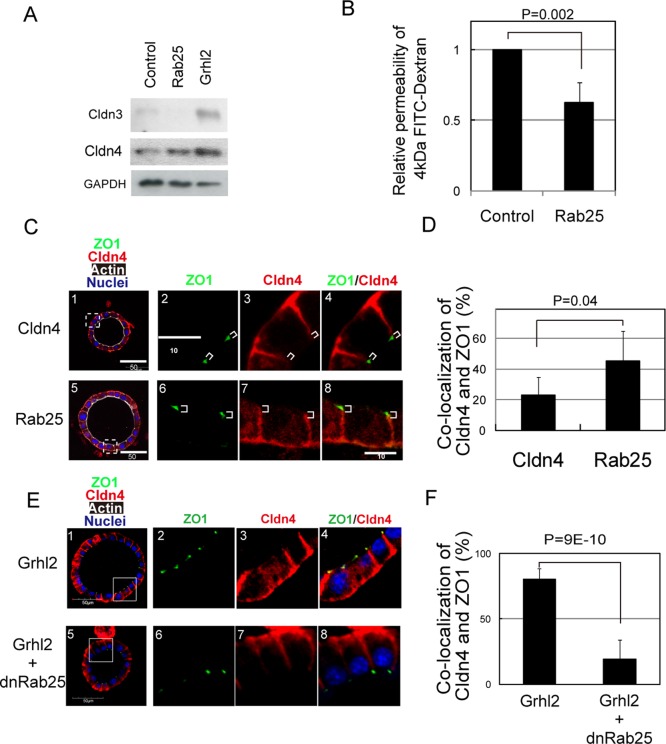
FIGURE 6:
Rab25 increases Cldn4 protein and regulates its localization at TJs. (A) Rab25 increases the level of Cldn4 protein. Western blot data demonstrate that Rab25 increases Cldn4 protein but not Cldn3. (B) Rab25 enhances barrier function of the monolayer of HPPL. Rab25 decreases paracellular efflux of 4-kDa FITC-dextran, indicating that the barrier function of HPPL monolayer is enhanced. The control HPPL and HPPL-Rab25 were cultured on Transwells and used to examined the efflux of FITC-dextran. Experiment was repeated three times independently. (C, D) Rab25 promotes the localization of Cldn4 at TJs. Cldn4 (red) is barely colocalized with ZO1 (green) in HPPL-Cldn4 (C1–C4), whereas it is colocalized with ZO1 in HPPL-Rab25 (C5–C8). More than 50 lateral membranes derived from five cysts were analyzed for localization of Cldn4 and ZO1. The result is shown in D, indicating that Rab25 significantly increases colocalization of Cldn4 and ZO1. (E, F) dnRab25 inhibits the localization of Cldn4 at TJs. Cldn4 (red) is colocalized with ZO1 (green) in HPPL-Grhl2 (E1–E4), whereas it is not colocalized with ZO1 in HPPL-Grhl2+Rab25 (E5–E8). More than 100 lateral membranes derived from 10 cysts were analyzed for localization of Cldn4 and ZO1. The result is shown in F, indicating that dnRab25 significantly inhibits colocalization of Cldn4 and ZO1.