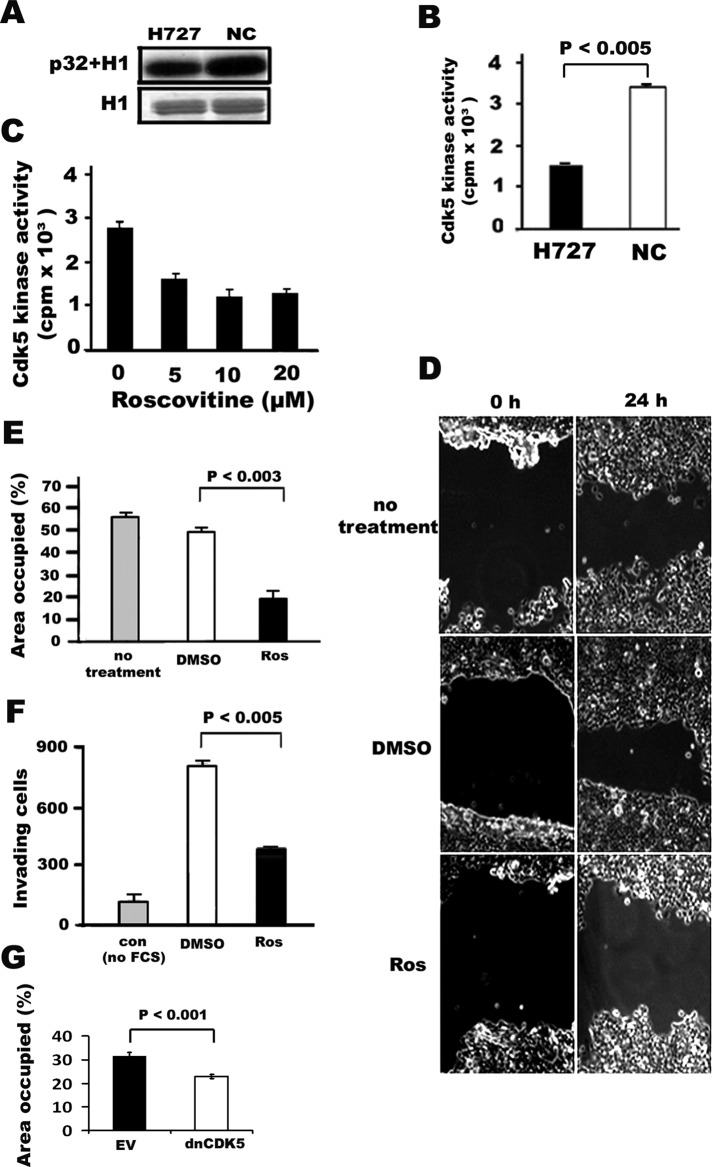
FIGURE 2:
Cdk5 activity, migration, and invasion of H727 lung cancer cells is blocked by the Cdk5 inhibitor roscovitine. (A) Cdk5 assay of H727 human lung cancer cells with H1 phosphorylation. Autoradiographs (top) of phosphorylated H1 band and the corresponding Coomassie blue–stained gels of H1 (bottom). (B) Quantification of Cdk5 activity. NCs were used as a positive control. (C) Inhibition of Cdk5 activity by roscovitine. The bar graph indicates means ± SD from three independent experiments. (D) Phase-contrast photomicrographs of wound-healing assay using human H727 lung cancer cells following treatment with the Cdk5 inhibitor roscovitine. The ability of cells to migrate to the wound area was compared at 0 h and 24 h. Panels illustrate cellular migration without treatment and with treatment using the solvent DMSO and 20 μM of roscovitine (Ros). (E) Quantification (bar graph) of the wound areas is expressed as the percentage of the initially bare area at 0 h that is occupied by the migrating cells at 24 h. The occupied area decreased from 60 to 20% when cells were treated with roscovitine (p < 0.003) as compared with cells treated with DMSO. The solvent DMSO had no effect when compared with no treatment. (F) Quantification (bar graph) of cell invasion assay. H727 cells in serum-free media were plated onto Boyden chambers with Matrigel and allowed to invade toward serum in the absence (no treatment) or presence of roscovitine (Ros) for 24 h. The number of cells that invaded in the presence of 20 μM of roscovitine was significantly decreased compared with cells without treatment (p < 0.005). Minimal invasion was seen when the cells were plated in serum containing media (con, control without concentration gradient between the chambers). Values represent the mean ± SD of three wells from three experiments. (G) Quantification (bar graph) of wound repair assay using H727 cells transfected with dnCDK5. EV, empty virus.