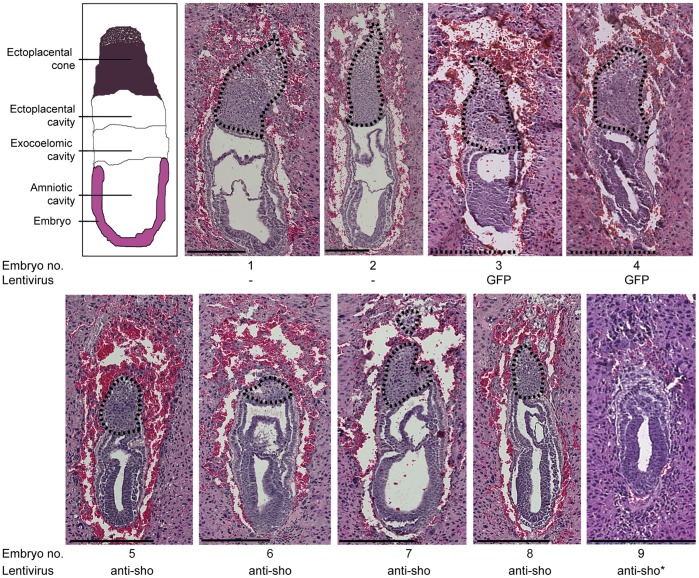
Figure 1. Histological analysis of E7.5 embryos.
E7.5 embryos were fixed and stained by hematoxylin, eosin, and saffron. Top left: schematic representation of a mouse E7.5 embryo. 1,2: FVB/N PrnpKO embryos. 3,4: FG12-injected FVB/N PrnpKO embryos. 5–8: LS2-injected FVB/N PrnpKO embryos. 3–8: embryos that were injected at the zygotic stage. 9: LS2-infected FVB/N PrnpKO embryos. *: infection performed at the blastocyst stage. Interesting features include i) the size differences between injected and non-injected embryos, ii) the relatively important hemorrhagic tissue that is totally surrounding the LS2-injected FVB/N PrnpKO embryos 5, 6 and 8, iii) the developmental defect of the ectoplacental cone (area surrounded using a dashed line ) of all the LS2-injected FVB/N PrnpKO embryos (5–8) that even leads to its nearly complete disappearance in embryo 6 and iv) the important developmental delay and the total disorganization of the extra-embryonic ectoderm and of the ectoplacental cone of embryo 9. Scale: 250 µm. Sho: Sprn.