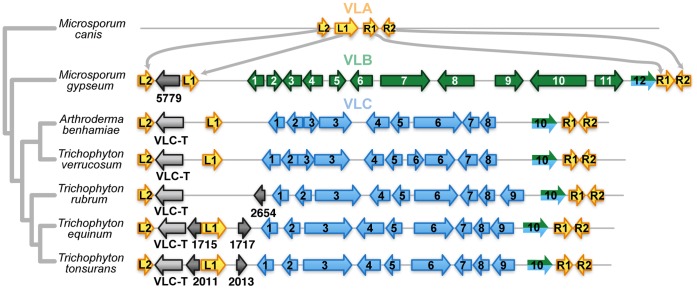
Figure 1. Synteny and the three distinct conformations of the variable locus.
The consensus species phylogeny of Microsporum canis, Microsporum gypseum, and Trichophyton spp. is shown on the left. The gene contents of the variable locus of each species are shown to the right of the species name. The yellow arrows represent the genes flanking the variable locus. Arrows with the same label (i.e., L1) represent homologous genes. The green arrows represent the genes in the variable locus in Microsporum gypseum. These genes are flanked by conserved genes L1, L2, R1, and R2. The blue arrows represent the genes found in the variable locus in the Trichophyton spp. The conserved genes, marked in yellow, also flank the Trichophyton spp. genes in the variable locus. However, in Microsporum canis, the conserved flanking genes (marked by yellow) are directly connected. The grey arrows represent lineage-specific intervening genes. Both the assemblages in Trichophyton spp. and M. gypseum share the flanking gene VLB-12/VLC-10 (marked half-green, half-blue). These arrows are drawn to scale.