Figure 1. The basic clock machinery consists of negative transcriptional-translational feedback loops.
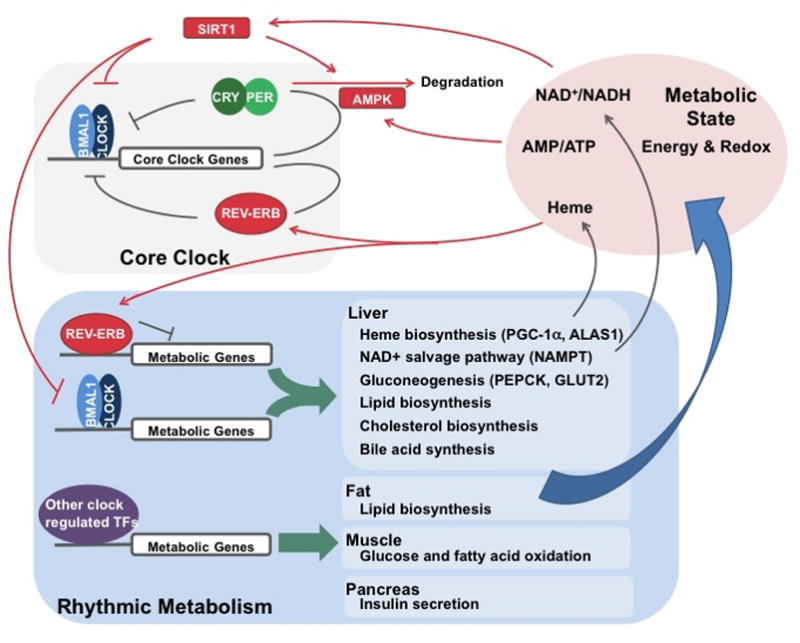
In the first loop, BMAL1/CLOCK drives Per/Cry transcription, while PER/CRY binds and inhibits transcriptional activity of BMAL1/CLOCK. In the second loop, BMAL1/CLOCK drives REV-ERB expression, which in turn represses Bmal1 transcription. Both loops are essential for maintaining circadian rhythm. In addition, post-translational modification, as shown for PER/CRY and REV-ERB, is also important in regulating clock activity. The core clock machinery can drive rhythmic behavioral and physiological activities, such as metabolism.
