Figure 3. The core clock machinery drives rhythmic metabolic activities and receives feedback from intracellular metabolites.
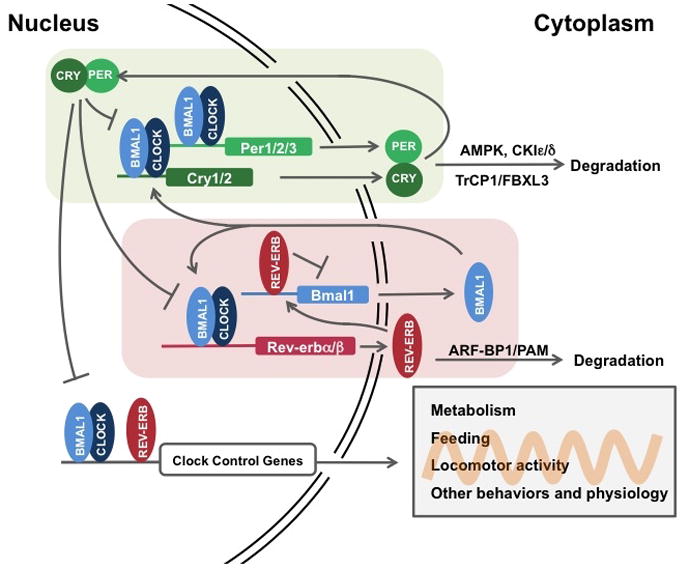
BMAL1/CLOCK and REV-ERB drive rhythmic metabolic outputs, including NAD+ and heme biosynthesis, while intracellular NAD+ and heme feedback on the clock through their sensors, SIRT1 and REV-ERB, respectively. Intracelluar AMP levels regulates the circadian clock through activation of AMPK and degradation of PER and CRY. The core clock also drives many metabolic pathways in different tissues, which also contribute to the intracellular metabolite pool and metabolic state.
