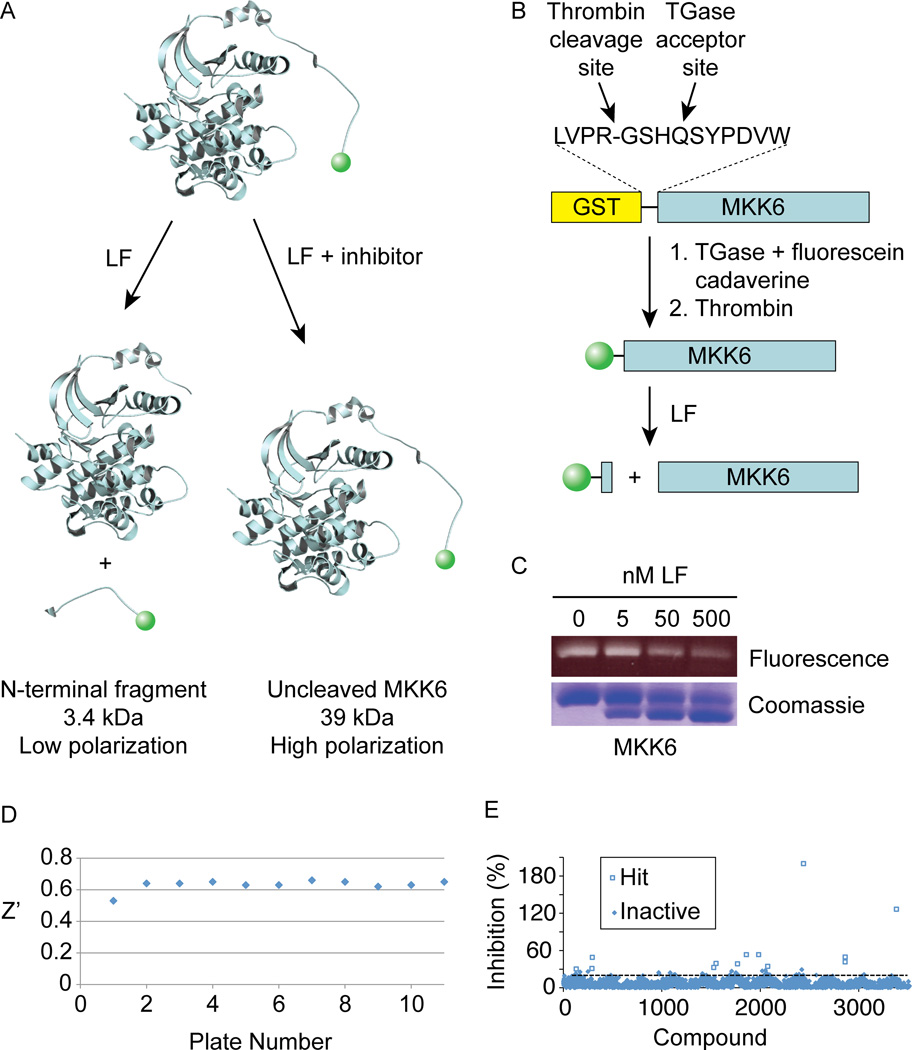
Figure 1. Identification of compounds that inhibit LF cleavage of full a length MKK using a FP based screen.
(A) Assay scheme. In the absence of inhibitors, MKK6 is cleaved, releasing a small fluorescent fragment having decreased FP. In the presence of an inhibitor, higher quantities of full length MKK6 provide an increased FP signal.
(B) Scheme for purification and N-terminal TGase-mediated labeling of MKK6.
(C) SDS-PAGE analysis of LF-cleaved N-terminally labeled MKK6. Fluorescein fluorescence (top panel) and total protein (bottom panel) is shown for 2 µM labeled MKK6 treated with the indicated concentrations of LF for 30 min at RT.
(D) Z’ values for each plate from the primary screen of 2835 molecules.
(E) Hit identification. Thirteen compounds showed greater than 30% inhibition relative to control reactions run in the absence of added compound.
See also Figure S1.