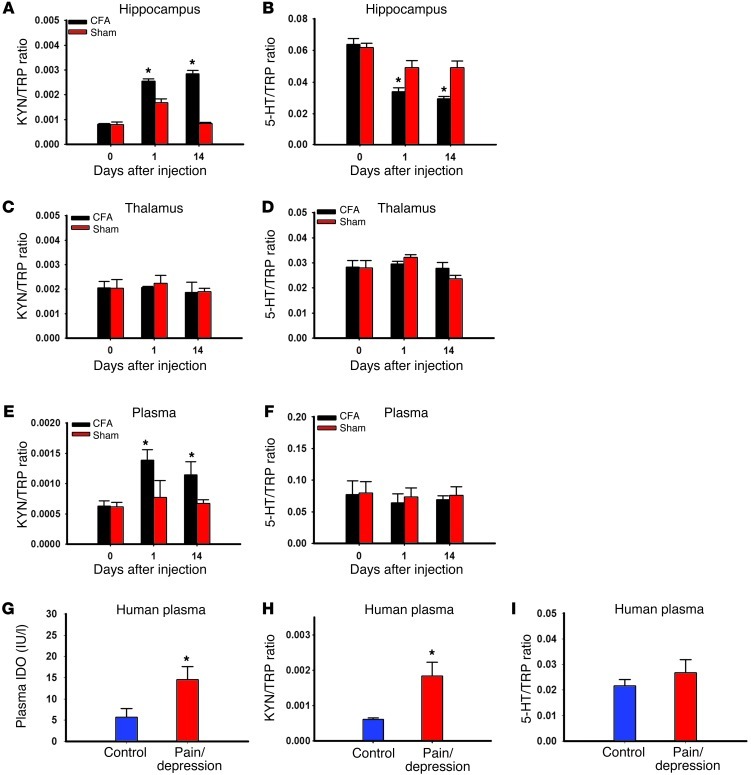
Figure 3. Altered tryptophan metabolites by IDO enzyme activity.
(A and B) The kynurenine (KYN)/tryptophan (TRP) ratio was increased (A), whereas the serotonin (5-HT)/TRP ratio was decreased (B), in the contralateral hippocampus of Wistar rats with CFA-induced arthritis as assayed by HPLC. Mean ± SEM, n = 6, *P < 0.05 compared with sham control. (C and D) The KYN/TRP ratio (C) and the 5-HT/TRP ratio (D) were not changed in the thalamus of Wistar rats with CFA-induced arthritis as assayed by HPLC. The plasma KYN/TRP ratio (E), but not the 5-HT/TRP ratio (F), was increased in Wistar rats with CFA-induced arthritis when both were examined on day 14. Mean ± SEM, n = 6, *P < 0.05 compared with sham control. The plasma IDO level (G; ELISA) and the KYN/TRP ratio (H; HPLC), but not the 5-HT/TRP ratio (I; HPLC), were elevated in patients with both chronic back pain and depression. Mean ± SEM, n = 13–20, *P < 0.05 compared with healthy control.