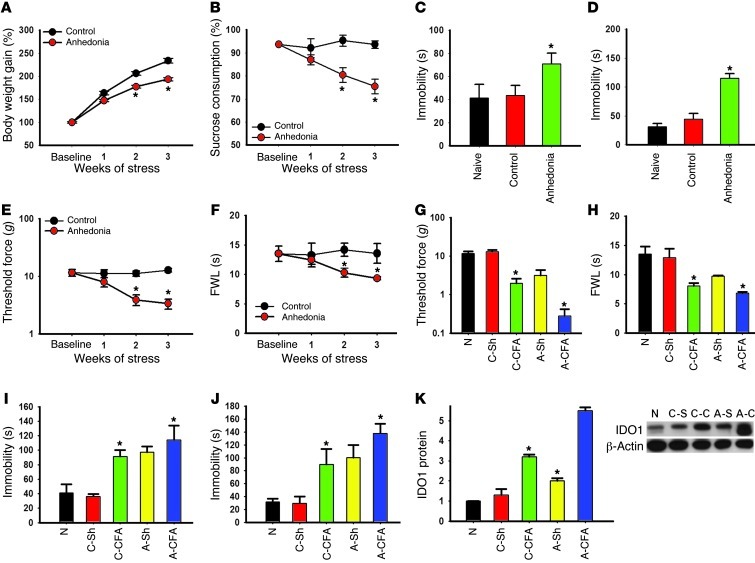
Figure 4. Relationship between anhedonic and nociceptive behavior.
(A) The body weight gain was calculated as the percentage of the initial (baseline) body weight. Anhedonic rats gained less weight than control rats. (B) Sucrose preference was calculated as the percentage of the total fluid intake over 24 hours. Sucrose preference was diminished in anhedonic rats. (C–F) The prolonged immobility time in FST (C) and TST (D) was associated with mechanical allodynia (E) and thermal hyperalgesia (F) in anhedonic rats. Data in A–F are mean ± SEM, n = 6 *P < 0.05 compared with control. (G–J) Mechanical allodynia (G) and thermal hyperalgesia (H) were exacerbated, and immobility time was prolonged, in FST (I) and TST (J) in anhedonic rats when examined at 7 days after the CFA-induced monoarthritis. (K) IDO1 protein expression was increased in anhedonic rats (A-Sh and A-CFA) as compared with control rats (C-Sh and C-CFA) with and without CFA injection. Data in G–K are mean ± SEM, n = 6, *P < 0.05 compared with sham control. N, naive.