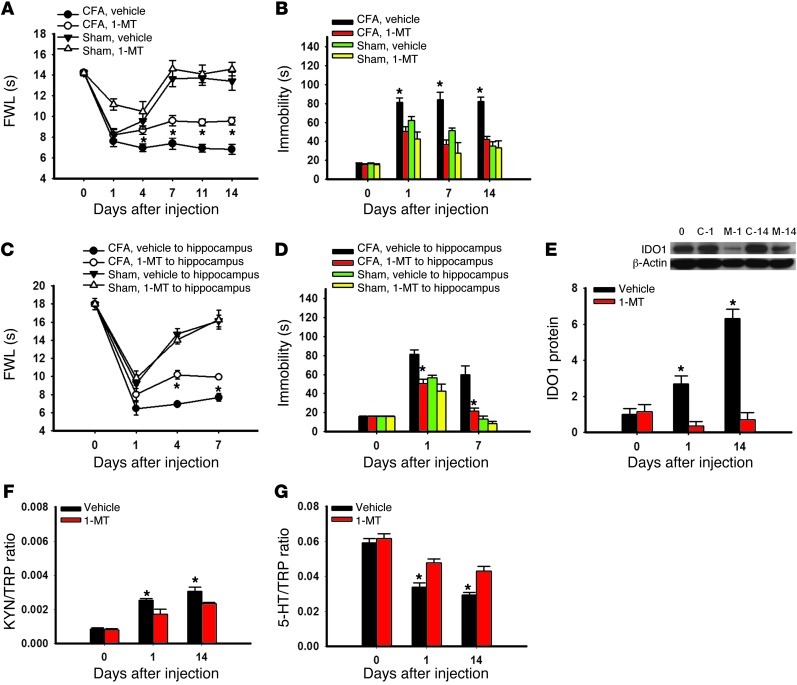
Figure 5. Effect of IDO1 inhibition on behavioral changes.
(A) Intraperitoneal injection of the IDO1 inhibitor 1-MT (10 mg/d), given twice daily for 14 consecutive days beginning immediately after the CFA injection, attenuated mechanical allodynia on the ipsilateral hind paw of rats. (B) The same 1-MT treatment regimen concurrently improved the immobility time in FST in the same rats. Mean ± SEM, n = 6, *P < 0.05 compared with vehicle control. (C and D) Intra-hippocampal microinjection of 1-MT (5 μg in 0.5 μl), once daily for 7 days beginning immediately after the CFA injection, also attenuated thermal hyperalgesia (C) on the ipsilateral hind paw of rats as well as reducing the immobility time in FST (D) in the same rats. Mean ± SEM, n = 6, *P < 0.05 compared with vehicle control. (E) IDO1 expression in the hippocampus was decreased in rats receiving a 14-day intraperitoneal administration of 1-MT (10 mg/d). Day 0, baseline (naive rats); C-1 and C-14, samples taken on day 1 and day 14 from rats with CFA-induced arthritis; S-1 and S-14, samples taken on day 1 and day 14 from control rats. β-Actin was used as loading control. Mean ± SEM, n = 6, *P < 0.05 compared with sham control. The same systemic 1-MT treatment regimen reduced the KYN/TRP ratio (F) and increased the 5-HT/TRP ratio (G) in the hippocampus. Mean ± SEM, n = 6, *P < 0.05 compared with vehicle control.