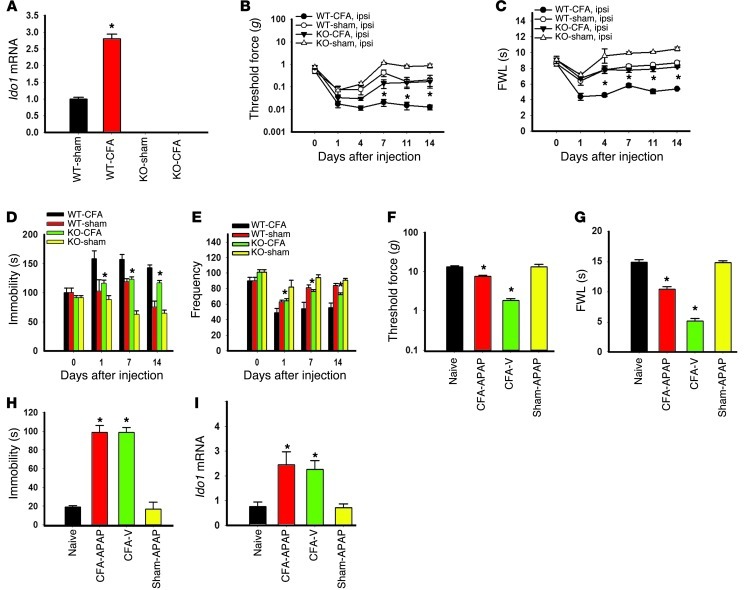
Figure 6. Effect of IDO-knockout on behavioral changes.
(A) IDO-knockout mice had no Ido1 mRNA expression (real-time PCR) in the hippocampus. Ido1 mRNA expression in wild-type mice was increased in the hippocampus after the CFA injection. Mean ± SEM, n = 6, *P < 0.05 compared with sham control. (B and C) Mechanical allodynia (B) and thermal hyperalgesia (C) on the ipsilateral hind paw were attenuated in IDO-knockout mice. (D and E) IDO-knockout also reduced the immobility time in FST (D) and the decreased frequency in OFT (E) in the same mice with CFA-induced arthritis. Mean ± SEM, n = 6, *P < 0.05 compared with wild-type mice. (F and G) Intraperitoneal injection of acetaminophen (APAP; 100 mg/kg), given once on day 14, attenuated ipsilateral mechanical allodynia (F) and thermal hyperalgesia (G) when mice were examined at 1 hour after the injection. Mean ± SEM, n = 6, *P < 0.05 compared with vehicle control. (H) The same APAP treatment did not change the immobility time in FST in the same rats. (I) Contralateral hippocampal Ido1 mRNA expression was increased after the CFA injection, which was not reversed by a single APAP treatment. Data in H and I are mean ± SEM, n = 6, *P < 0.05 compared with vehicle control.