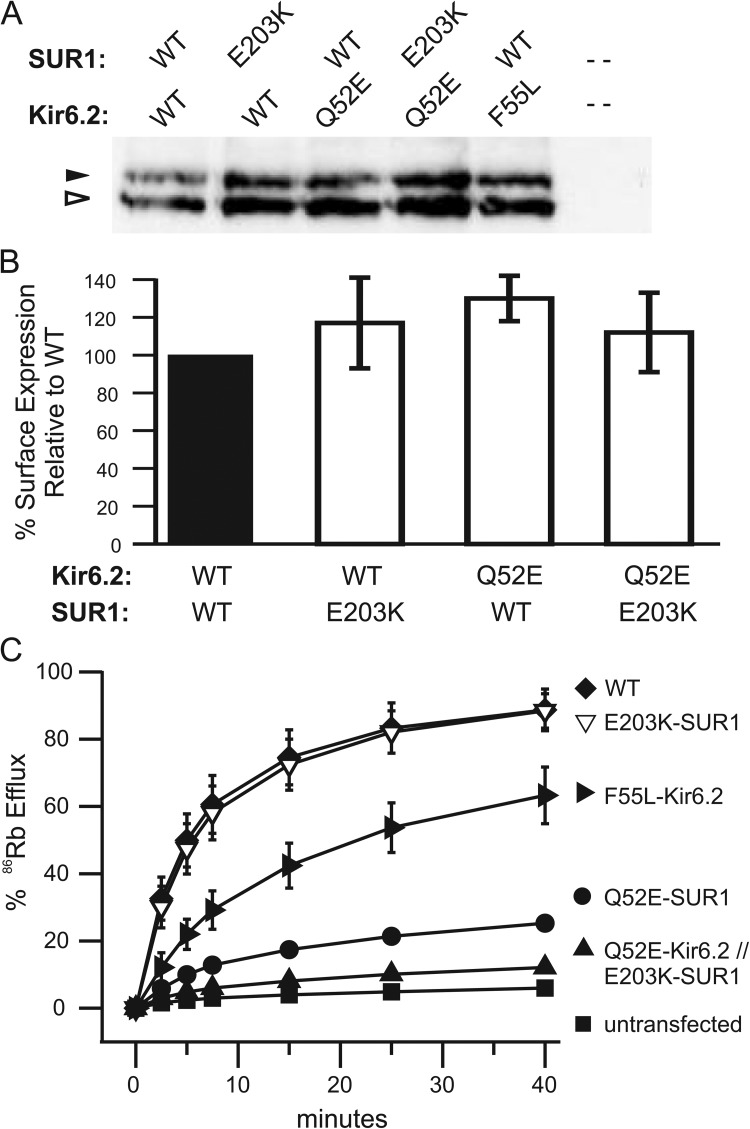
Figure 8.
Increased ATP sensitivity in channels formed by E203K-SUR1 and Q52E-Kir6.2 compromise their ability to open in response to metabolic inhibition. (A and B) Processing and surface expression of KATP channels were assessed in COSm6 cells transfected with WT or mutant channels. (A) Western blot of SUR1 using anti-SUR1 antibody as described in Materials and methods. The complex-glycosylated, mature form of SUR1 (a proxy for surface expression) is indicated by the closed arrowhead, and the core-glycosylated, immature form is indicated by the open arrowhead. Mutations at Q52E-Kir6.2 and/or E203K-SUR1 do not disrupt protein trafficking. (B) KATP surface expression was quantified using chemiluminescence assays. Mutations at Q52E-Kir6.2 or E203K-SUR1 or both do not affect the number of channels at the cell surface. Control F55L-Kir6.2 channels also have WT-like surface expression (Lin et al., 2006b). Error bars represent SEM; n = 3. (C) Mean 86Rb+ efflux profile from COSm6 cells transiently expressing WT or mutant channel subunits. Efflux was measured in Ringer’s solution after metabolic inhibition (i.e., decreased intracellular ATP production). Channels composed of Q52E-Kir6.2 with and without E203K-SUR1 show significantly diminished efflux compared with controls, WT and F55L-Kir6.2; the latter control was included because it has decreased intrinsic Po (∼0.11) but normal ATP sensitivity and surface expression. Error bars represent SEM for n = 3 experiments, except F55L-Kir6.2, which represents the difference between n = 2 experiments. Some error bars are smaller than the symbols.