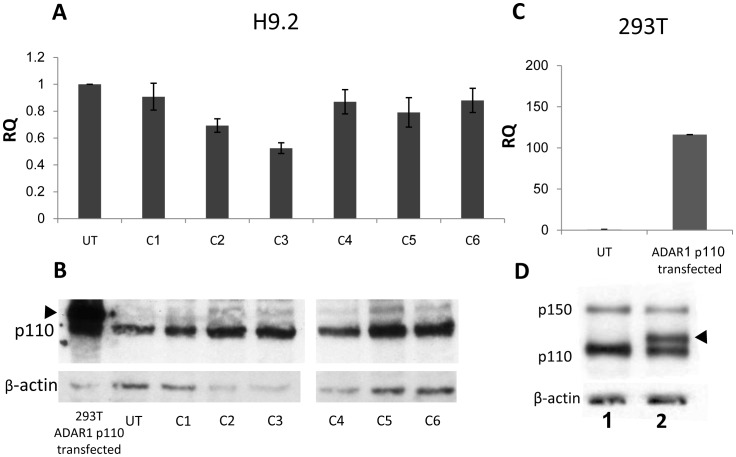
Figure 4. Transfection of ADAR1-p110 gene into hESC line H9.2.
Attempts to generate stable hESC lines H9.2 overexpressing ADAR1-p110 failed: The pcDNA3.1/HisC plasmid, expressing ADAR1-p110 conjugated to His-tag and Xpress epitope at the amino end of the protein (which adds approximately 6 kDa to the protein) under the CMV promoter, was transfected into H9.2 hESCs. A similar plasmid was transfected into 293T cells for validation of plasmid functionality. H9.2 transfected cells were cultured on Neomycine (Neo) resistant Mouse Embryonic Fibroblast (MEF) feeder cells, and selection was performed with 50 µg/ml Neo for 10 days. Neo-resistant hESC clones were isolated and expanded. RNA and protein extracts were generated from 40 selected hESC clones and subjected to (A) QRT-PCR analysis and (B) Western Blot analysis. Representative data for 6 Neo-resistant hESC clones (C1–C6) are shown here relative to untransfected hESC H9.2 samples. For the Western Blot a positive control of 293T transfected cells, overexpressing ADAR1-p110 was added (left lane). Arrow head indicates the exogenous His-tag conjugated ADAR1-p110. No hESC Neo-resistant clone showed significant overexpression of ADAR1-p110 isoform following transfection and Neo-selection. 293T cells were harvested 4 days post transfection. RNA and protein were extracted from untransfected (UT) and transfected cells. ADAR1-p110 expression was analyzed by (C) QRT-PCR and (D) Western Blot analysis, lane 1– control untransfected cells, lane 2– transfected cells. Results show that ADAR1-p110 overexpression could be induced in 293T cells but not in selected hESC clones.