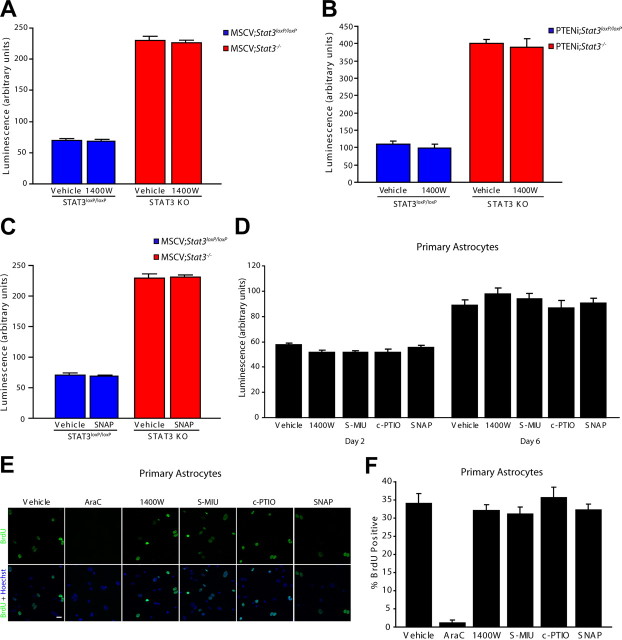
Figure 4.
iNOS is not required for the proliferation of control and PTEN-deficient astrocytes. A, Population growth of MSCV;Stat3loxP/loxP and MSCV;Stat3−/− astrocytes was assessed as in Figure 3C. Pharmacological inhibition of iNOS with 1400W had little or no effect on the population growth of MSCV;Stat3loxP/loxP and MSCV;Stat3−/− astrocytes compared with vehicle treatment (n = 3). B, Population growth of PTENi;Stat3loxP/loxP and PTENi;Stat3−/− astrocytes was assessed as in Figure 3C. Pharmacological inhibition of iNOS with 1400W had little or no effect on the population growth of PTENi;Stat3loxP/loxP and PTENi;Stat3−/− astrocytes compared with vehicle treatment (n = 3). C, Population growth of MSCV;Stat3loxP/loxP and MSCV;Stat3−/− astrocytes was assessed as in Figure 3C. The NO donor SNAP had little or no effect on the population growth of MSCV;Stat3loxP/loxP and MSCV;Stat3−/− astrocytes compared with vehicle treatment (n = 3). D, Population growth of primary mouse astrocytes was assessed as in Figure 3C. Pharmacological inhibitors and activators of the iNOS pathway had little or no effect on the population growth of primary mouse astrocytes compared with vehicle treatment (n = 3). E, Primary mouse astrocytes treated with inhibitors and activators of the iNOS pathway were subjected to immunocytochemistry using the BrdU antibody. Inhibition or activation of the iNOS pathway had little or no effect on BrdU incorporation of primary mouse astrocytes compared with vehicle treatment. In control experiments, the nucleoside analog AraC substantially reduced BrdU incorporation in primary astrocytes compared with vehicle treatment. Scale bar, 20 μm. F, Primary mouse astrocytes analyzed as in E were quantified for the percentage of BrdU-positive cells. Inhibition or activation of the iNOS pathway had little or no effect on BrdU incorporation in primary astrocytes. In control experiments, the nucleoside analog AraC significantly reduced BrdU incorporation compared with vehicle treatment (ANOVA, p < 0.0001, n = 3). KO, Knock-out.