Figure 7.
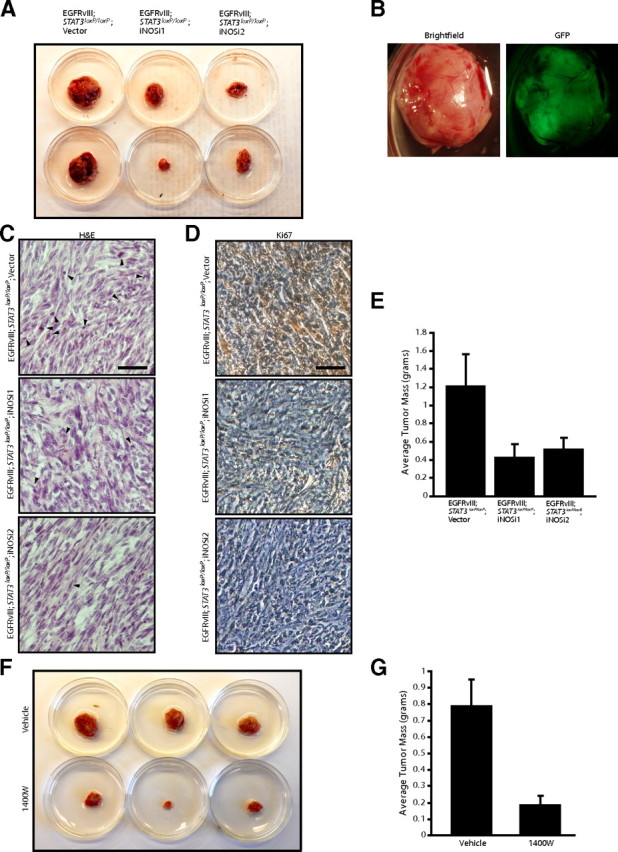
iNOS is required for the ability of EGFRvIII-expressing astrocytes to form tumors in vivo. A, Control and iNOS knockdown EGFRvIII;Stat3loxP/loxP astrocytes were injected subcutaneously into SCID mice. Four weeks after injection, tumors were removed, measured, and stained. iNOS knockdown reduced tumor size. B, Representative excised subcutaneous tumor revealed that masses removed were GFP positive and derived from injected cells. C, Tumors derived from control and iNOS knockdown EGFRvIII;Stat3loxP/loxP astrocytes were analyzed by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. Control EGFRvIII;Stat3loxP/loxP astrocytes showed histological features of neoplastic transformation, including nuclear atypia, hypercellularity, and frequent mitotic figures (arrowheads), although these features were less prominent in iNOS knockdown tumors. Scale bar, 200 μm. D, Tumors derived from control and iNOS knockdown EGFRvIII;Stat3loxP/loxP astrocytes were analyzed by immunohistochemical analyses using the Ki67 antibody. Tumors derived from control EGFRvIII;Stat3loxP/loxP astrocytes had substantially greater Ki67 immunoreactivity compared with tumors derived from iNOS knockdown EGFRvIII;Stat3loxP/loxP astrocytes. Scale bar, 200 μm. E, Average tumor mass of tumors from A was measured. iNOS knockdown significantly reduced the mass of EGFRvIII;Stat3loxP/loxP tumors (ANOVA, p < 0.05, n = 33 animals). F, EGFRvIII;Stat3loxP/loxP astrocytes were injected subcutaneously into SCID mice, and the iNOS inhibitor 1400W or vehicle control was locally administered. Four weeks after initial injections, tumors were removed, measured, and stained. Treatment with the iNOS inhibitor 1400W substantially reduced tumor size. G, Average tumor mass of tumors from F was measured. Treatment with the iNOS inhibitor 1400W substantially reduced the mass of EGFRvIII;Stat3loxP/loxP tumors (t test, p < 0.005, n = 20 animals). Two animals in the 1400W-treated cohort did not have detectable tumors at the endpoint.
