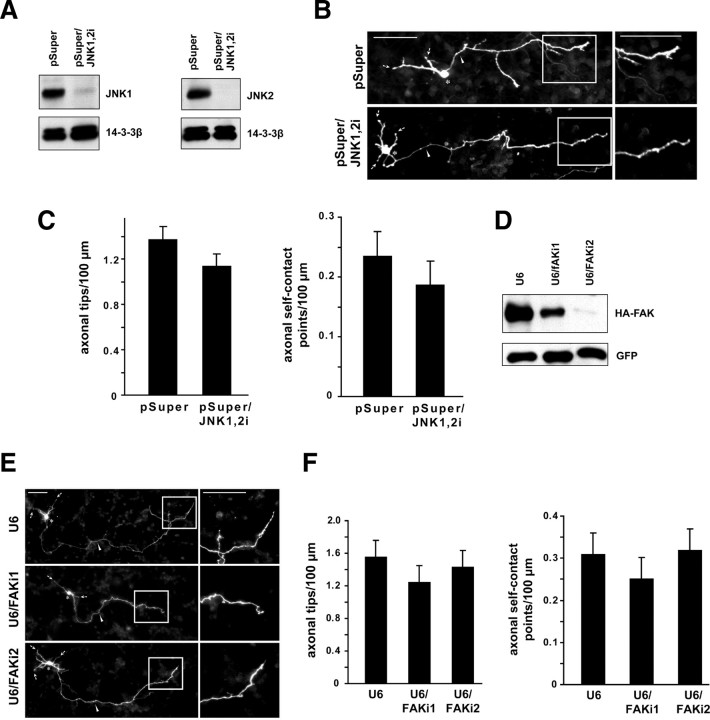
Figure 3.
JNK knockdown or FAK knockdown do not appear to induce axon branching or self-contact. A, Left, Lysates of HEK293T cells transfected with the FLAG–JNK1 expression plasmid and the pSuper/JNK1,2i or control pSuper RNAi plasmid were immunoblotted using the FLAG and 14-3-3β antibodies. Right, Lysates of HEK293T cells transfected with the FLAG–JNK2 expression plasmid and the pSuper/JNK1,2i or control pSuper RNAi plasmid were immunoblotted using the FLAG and 14-3-3β antibodies. B, Granule neurons transfected with the pSuper/JNK1,2i or control pSuper RNAi plasmid together with the GFP expression plasmid were analyzed as in Figure 1B. Scale bars, 50 μm. C, Quantification of axon branching of granule neurons treated as in B. JNK knockdown did not significantly alter either the number of axonal tips or the number of axonal self-contact points per hundred micrometers. A total of 149 neurons were measured. D, Lysates of HEK293T cells transfected with the HA–FAK expression plasmid and the U6/FAKi1, U6/FAKi2, or control U6 RNAi plasmid were immunoblotted using the HA and GFP antibodies. E, Granule neurons transfected with the U6/FAKi1, U6/FAKi2, or control U6 plasmid together with the GFP expression plasmid were analyzed as in Figure 1B. Scale bars, 50 μm. F, Quantification of axon branching of granule neurons treated as in E. FAK knockdown with either hairpin did not significantly alter the number of axonal tips or the number of axonal self-contact points per hundred micrometers. A total of 232 neurons were measured.