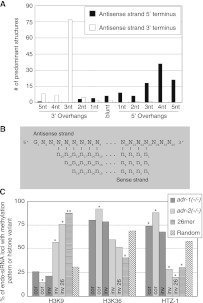
Figure 5.
ADAR-affected 26G loci have small RNA reads that can base-pair in specific structures and have histone modification patterns associated with transcriptional silencing. (A) Bar height indicates number of termini with a given terminus from putative Inverse 26G structures, relative to the antisense strand. If multiple reads could form different structures at a given location, the structure with the predominate read was analyzed. (B) Consensus structure of predominant structures from 26G loci. Nearly all reads had a 5′ guanosine, while other positions varied. (C) Histone modification and histone variant patterns for various groups of endo-siRNA loci. χ2 tests compare patterns from each group to the random data set, with P-values < 0.05 (*) or < 1 × 10−10 (**). (cor) Correlated loci, (inv) Inverse loci, (inv 26) Inverse 26G loci.