Figure 11. CCL2 induces shuttling of β-catenin between PECAM-1 and the AJ in HBMVEC such that the AJ and monolayer integrity are transiently disrupted.
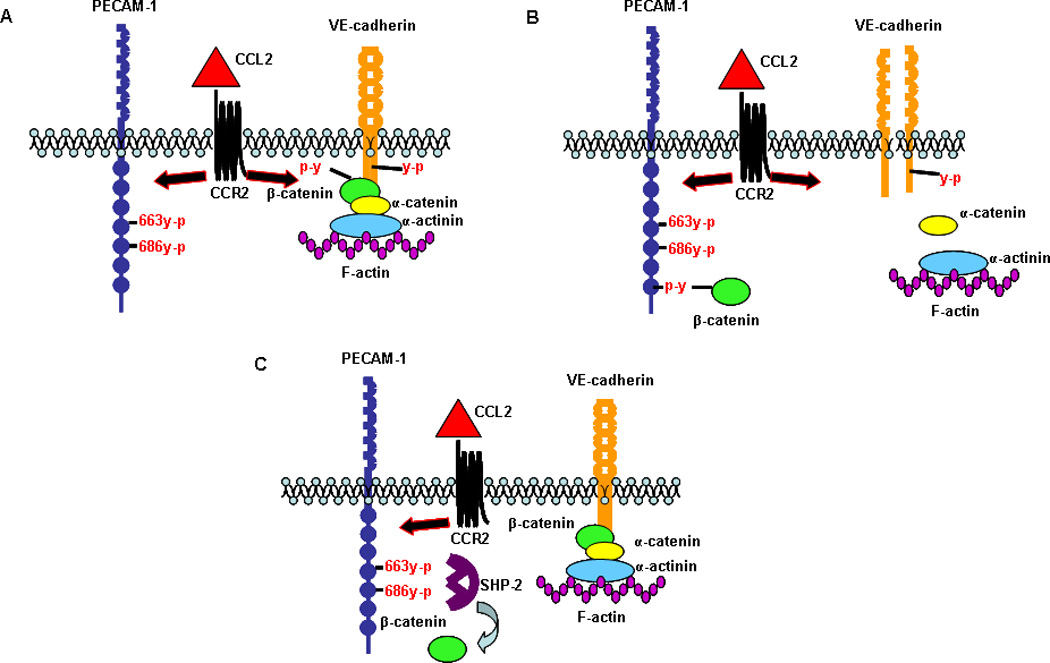
(A) CCL2 induces tyrosine phosphorylation of VE-cadherin, β-catenin, and PECAM-1 after 30 minutes of exposure. (B) VE-cadherin and β-catenin tyrosine phosphorylation result in loss of AJ integrity. Tyrosine phosphorylated β-catenin binds to PECAM-1 and is sequestered at the plasma membrane. (C) Tyrosine phosphorylation of PECAM-1 in response to CCL2 creates a docking site for the protein phosphatase SHP-2. Binding of SHP-2 to PECAM-1 promotes dephosphorylation of β-catenin by SHP-2 and release of β-catenin from PECAM-1. β-catenin reassociates with VE-cadherin and reforms the AJ. Thus, CCL2 mediates a transient disruption of the AJ through the temporary sequestration of β-catenin by PECAM-1 at the plasma membrane.
