Figure 4. CCL21-induced HMVEC migration and tube formation is suppressed by PI3K inhibition.
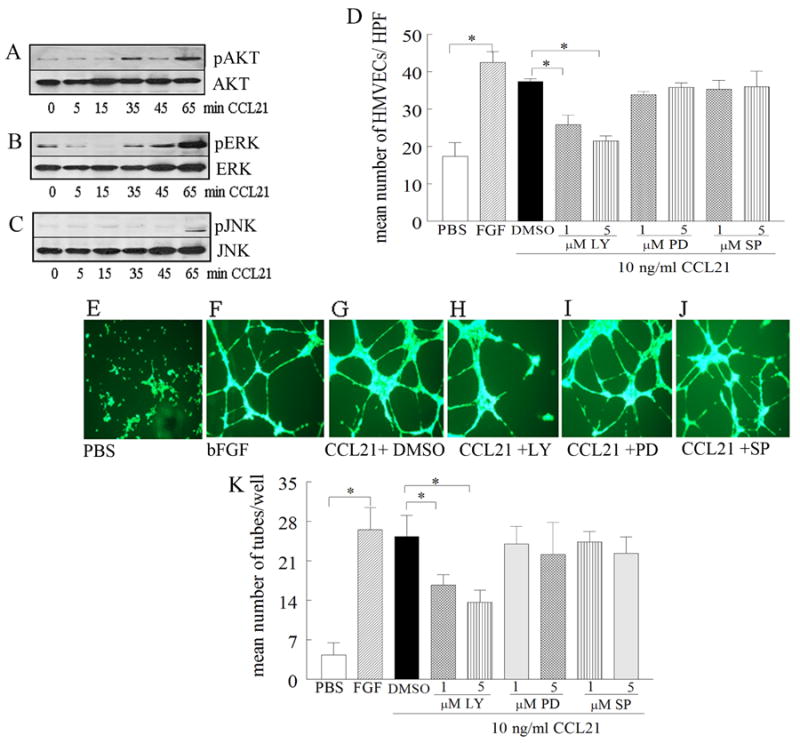
To determine the mechanism of CCL21 in HMVEC migration, cells were stimulated with CCL21 (10 ng/ml) for 0-65 minutes, and cell lysates were probed for pAKT (A), pERK (B), or pJNK (C) (n=3). D. To determine signaling pathways associated with CCL21 HMVEC migration, cells were treated with (1 or 5 μM) of the identified chemical inhibitors for PI3K (LY294002), ERK (PD98059) or JNK (SP600125) for 2h. To examine the mechanism of CCL21-induced tube formation, HMVECs were incubated with inhibitors (1 or 5 μM) to PI3K (LY294002), ERK (PD98059), JNK (SP600125) or DMSO for 45 minutes at 37°C prior to adding to polymerized matrigel. CCL21 (10ng/ml) was then added to the wells and the plate was incubated for 16h at 37°C (in triplicate). Photomicrographs taken of representative wells treated with PBS (E), FGF (20 ng/ml) (F), CCL21 (10ng/ml) plus DMSO (G), CCL21 (10ng/ml) plus LY294002 (5 μM) (H), CCL21 (10ng/ml) plus PD98059 (5 μM) (I) and CCL21 (10ng/ml) plus SP600125 (5 μM) (J). K. demonstrates mean number of tubes/well determined in E-J. Values are the mean ± SE, n=3. * represents p <0.05.
