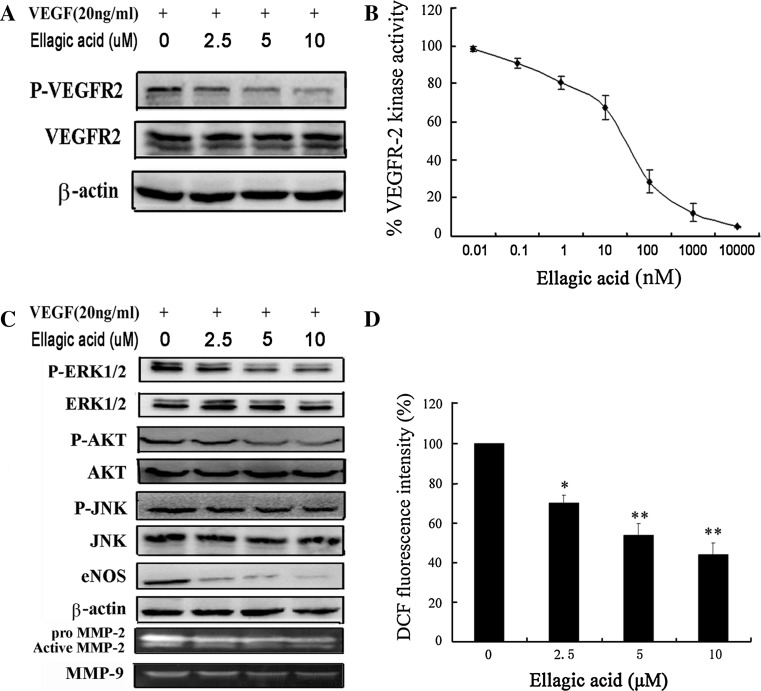
Fig. 4.
Ellagic acid attenuated VEGFR-2 tyrosine kinase activity and VEGFR-2 signaling pathway. a Ellagic acid reduced the phosphorylation of VEGFR-2 in VEGF-stimulated HUVECs. Endothelial cells were pre-cultured with ellagic acid at different concentrations for 24 h with the stimulation of VEGF (20 ng/ml). Expressions of VEGFR-2 and P-VEGFR2 were then examined by western blotting assay. It was found that P-VEGFR2 expression was markedly reduced, while the total level of VEGFR-2 was unaffected after the treatment of ellagic acid. b Ellagic acid suppressed VEGFR-2 kinase activity. VEGFR-2 and various concentrations of ellagic acid were incubated in kinase reaction buffer in 96-well plate coated with a poly-Glu-Tyr substrate. Phosphorylation of the substrate was monitored with a purified phosphotyrosine specific monocolonal antibody conjugated to horseradish peroxidase followed by chromogenic reaction with horseradish peroxidase substrate. Data are presented as a percentage of the control (values represent means ± SD, n = 3). c Ellagic acid inhibited VEGFR-2 downstream signaling molecules, including P-ERK/ERK, P-AKT/AKT, P-JNK/JNK, and e-NOS in a dose-dependant manner. Besides, the expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 were also inhibited after ellagic acid administration. d The HUVECs intracellular ROS level was detected by DCFH-DA staining assay. The results showed that the intracellular ROS level was significantly decreased after ellagic acid treatment (values represent means ± SD, n = 6, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus untreated control)