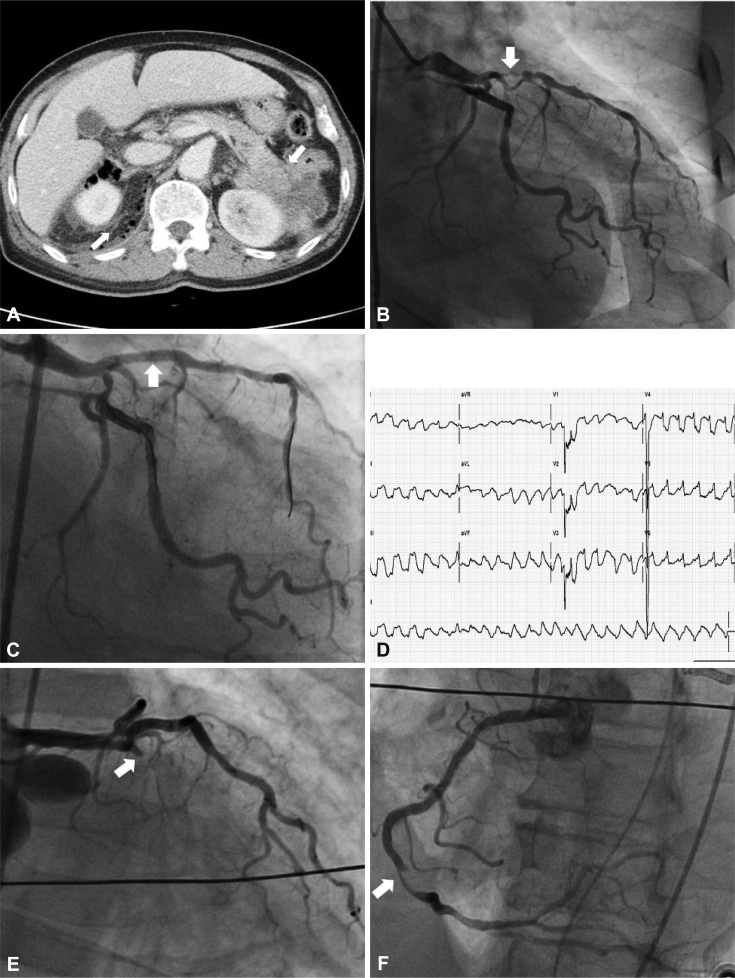
Fig. 2.
A case of simultaneous acute thrombosis in stent and native coronary artery. A: a CT scan of the abdomen reveals a pericolic abscess with pneumoretroperitoneum at the right perirenal space and a pancreatic tail mass invading into the left kidney (arrow). B: anterioposterior view; coronary angiography reveals a near total occlusion in the proximal LAD (arrow) which triggered intractable cardiogenic shock in this patient. C: right anterior oblique caudal view; the lesion was successfully revascularized (arrow). D: electrocardiogram at the event shows pulseless ventricular tachycardia. LAD: left anterior descending artery. E: emergency coronary angiography at the event identified a total occlusion of the proximal LAD stent with an extensive thrombus (arrow). F: left anterior oblique view; the patient had also developed a new thrombus in the distal right coronary artery that had not been seen during the previous angiography (arrow).