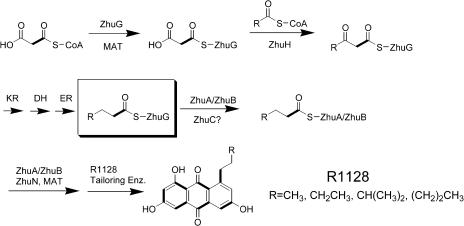
Figure 3. Proposed Priming Mechanisms for R1128 PKS.
An independent loading module consisting of ZhuG, ZhuH, and ZhuC can generate an alkylacyl-ZhuG intermediate (boxed) from malonyl-CoA and short chain acyl-CoAs such as propionyl-CoA and isobutyryl-CoA. The precursor selectivity is determined by the KSIII analog ZhuH. Ketoreductase, dehydratase, and enoylreductase associated with FAS are presumed to transformed the β-ketoacyl-ZhuG moiety into alkylacyl-ZhuG. The alkylacyl-ZhuG is then able to prime the minimal PKS module (consisting of the ZhuB [KS], ZhuA [CLF], ACP [ZhuN], and MAT) and initiate polyketide synthesis. The mechanism by which the transacylation occurs is not known and is possibly catalyzed by unassigned, but essential, enzyme ZhuC. Homologs of ZhuG, ZhuH, and ZhuC are present in the frn PKS (FrnJ, FrnK, and FrnI, respectively) as well.