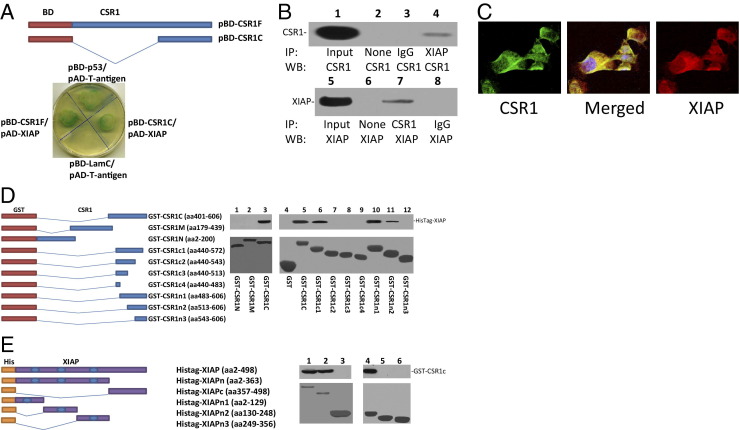
Figure 1.
The C-terminus of CSR1 binds XIAP. A: Constructs of full-length CSR1 (pBD-CSR1F) and the CSR1 C-terminus (pBD-CSR1c) bait domains for yeast two-hybrid analysis. Yeast cotransformed with pBD-CSR1F and pBD-CSR1c with pAD-XIAP were grown on an SD agar plate with high-stringency nutrient selection (SD/-Leu/-Trp/-His/-Ade). B: Coimmunoprecipitation of XIAP or CSR1 using antibodies specific for CSR1 or XIAP. Images represent the immunoprecipitates separated by SDS-PAGE and incubated with the indicated antibodies. C: Immunofluorescence staining of RWPE-1 cells with antibody against XIAP (red) b and antibody against CSR1 (green). D: GST-fusion proteins were used to map the XIAP-binding motif of CSR1. Left: CSR1 deletion mutants with GST expression vectors. Right: Representative binding assays performed with GST or GST-CSR1 deletion mutants and XIAP from PC3 cell (lanes 1 to 3) or HisTag-XIAP (lanes 4 to 12) lysate. Top panel: Immunoblots with antibodies specific for XIAP. Bottom panel: Coomassie staining of fusion proteins. E: Fusion proteins were used to map the CSR1-binding motif of XIAP. Left: XIAP deletion mutants with His-tag expression vectors. Right: Representative binding assays performed with HisTag-XIAP or deletion mutants and GST-CSR1c. Top panel: Immunoblots with antibodies specific for the CSR1 C-terminus. Bottom panel: Coomassie staining of proteins. Lane 1, HisTag-XIAP; lane 2, HisTag-XIAPn; lane 3, HisTag-XIAPc; lane 4, HisTag-XIAPn1; lane 5, HisTag-XIAPn2; and lane 6, HisTag-XIAPn3.