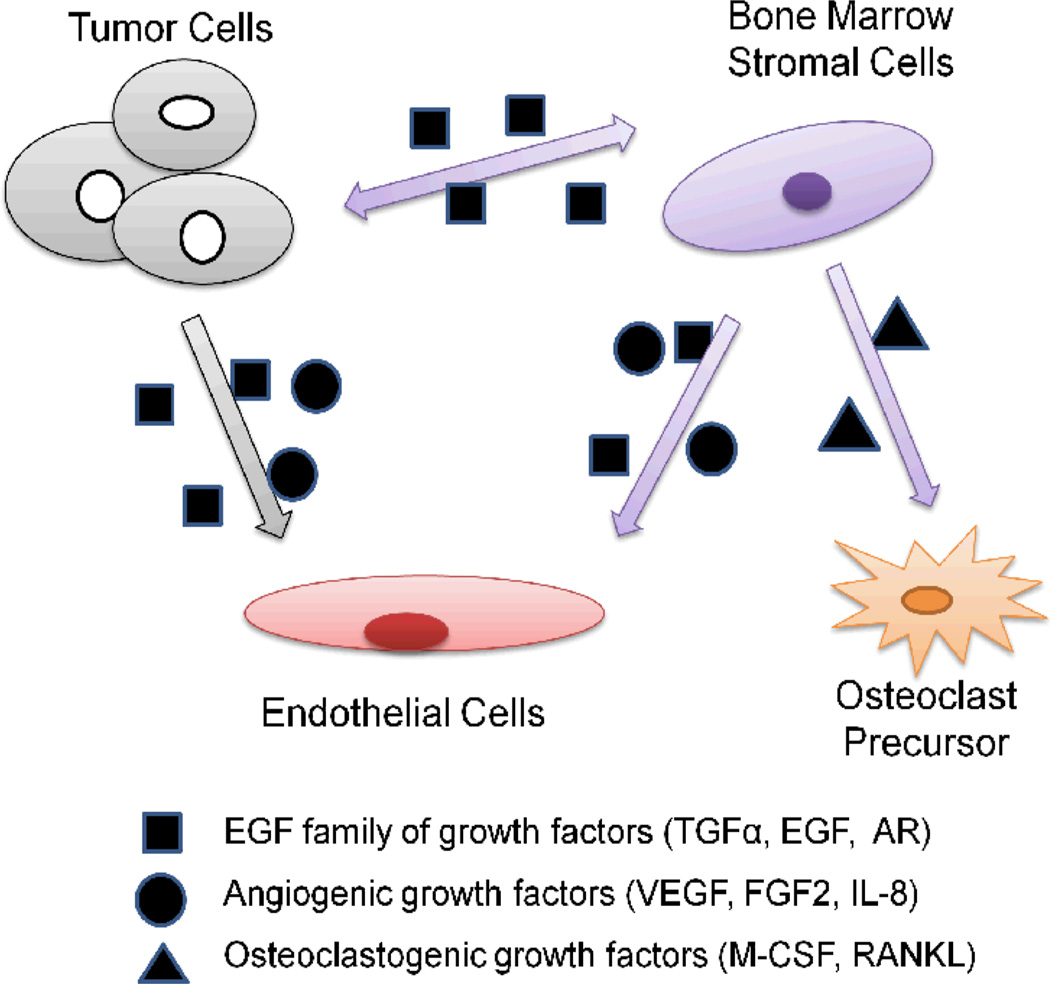
Fig. 1.
Autocrine and paracrine circuits of EGF/EGFR signaling in tumor microenvironment. Cancer cells secrete EGF family of growth factors that can act directly on endothelial cells. Also, EGF family of ligands for EGFR induce the expression of osteoclastogenic factors in bone marrow stromal cells that promote maturation and activation of osteoclasts, leading to bone destruction as well as the formation of bone metastases. In addition, bone marrow stromal cells produce EGF family of growth factors and angiogenic growth factors that can act on both endothelial cells and tumor cells. TGF-α, transforming growth factor α; AR, androgen receptor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; FGF2, fibroblast growth factor 2; IL-8, Interleukin-8; M-CSF, macrophage colony-stimulating factor; RANKL, receptor activator for nuclear factor κB ligand.