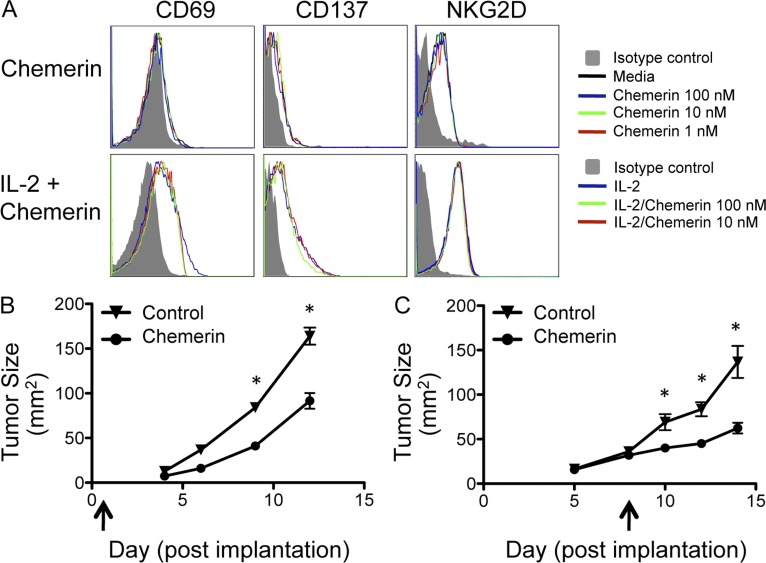
Figure 4.
Effects of exogenous chemerin on NK cell activation and tumor growth. (A) Untouched murine NK cells were isolated using the MACS NK Isolation kit II (Miltenyi Biotec) and cultured with or without 25 ng/ml IL-2 and/or active murine chemerin using the indicated conditions for 24 h. NK cells were then evaluated by flow cytometry for the activation phenotype. (B and C) Daily intratumoral injections of control (PBS or murine serum albumin) or recombinant active chemerin (25–250 ng/dose) were initiated at the time of tumor cell implantation (B) or after palpable tumors had established (C), as indicated by the arrows. *, P < 0.05 comparing tumor size (mean ± SEM) in chemerin injection versus control by two-tailed Student’s t test. Data are representative of three experiments (B) or more than five experiments (C), with cohorts of more than three mice per group.