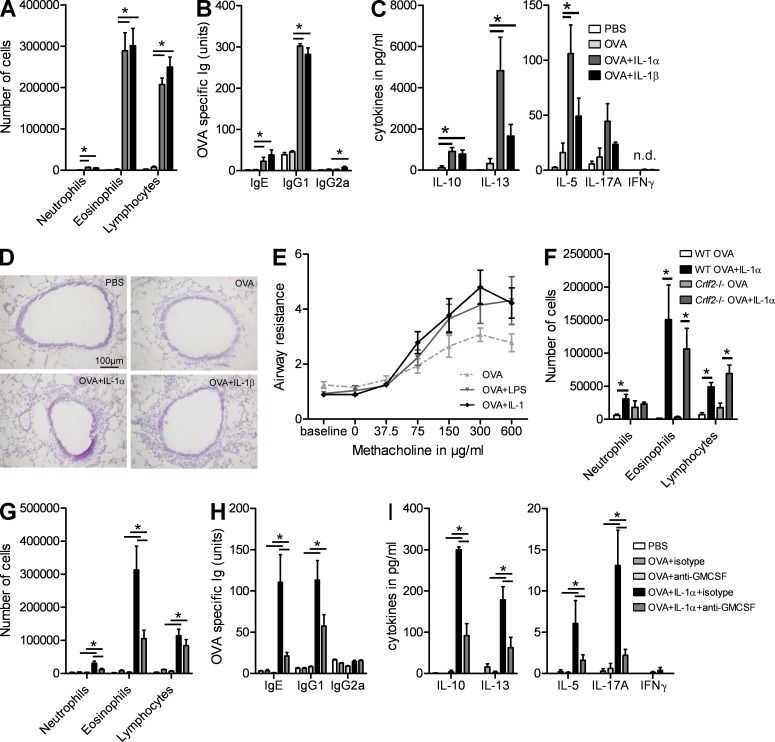
Figure 4.
IL-1α is sufficient to promote sensitization to inhaled protein antigens. (A–E) C57BL/6 mice were sensitized on day 0 with OVA in the presence of IL-1α, IL-1β, or PBS. Mice were challenged with OVA aerosols on days 10–12. (A) Differential cell counts were determined 24 h after the last challenge. (B) Levels of serum OVA–specific Igs. (C) Cytokine levels in MLN cells restimulated for 4 d with OVA. (D) PAS staining of lung sections. (E) Bronchial hyperreactivity was analyzed in mice sensitized with OVA + IL-1 or OVA + LPS. (F) C57BL/6 and Crlf2−/− mice were sensitized with OVA or with OVA + IL-1α and were exposed to OVA aerosols. Differential cell counts were determined 24 h after the last challenge. (G–I) C57BL/6 mice sensitized with OVA in the presence or absence of IL-1α and injected with anti–GM-CSF or isotype control antibodies were challenged with OVA aerosols. (G) Differential cell counts were determined 24 h after the last challenge. (H) Levels of serum OVA-specific Igs. (I) Cytokine levels in MLN cells restimulated for 3 d with HDM. *, P < 0.05. Results show one representative experiment out of three. Five mice/group were used. Results are shown as mean ± SEM.