Figure 2. Mechanisms by which histone tail arginine methylation regulates transcription.
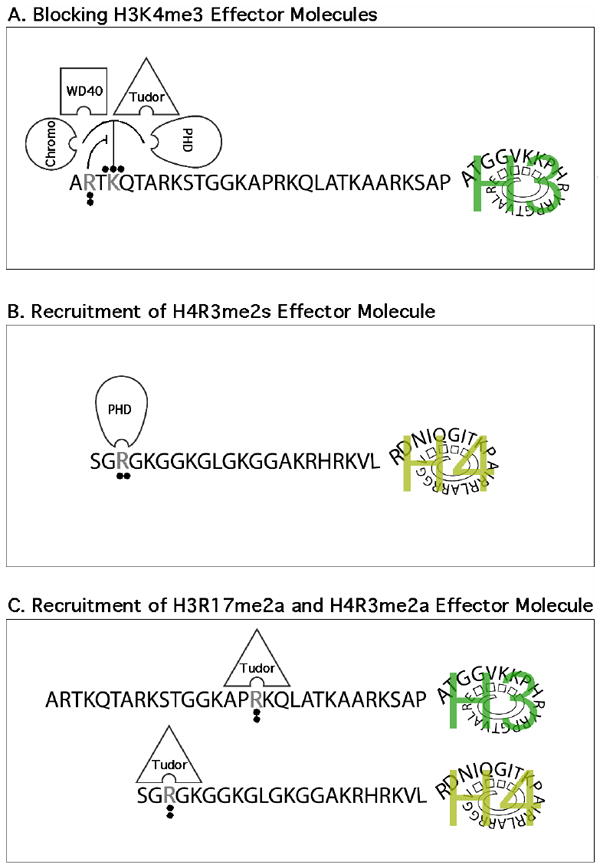
(A) The symmetrical dimethylation of H3R2 blocks the binding of H3K4me3 effector molecules. In addition, the H3R2me2a mark prevents methylation of H3K4me3 by MLL1. (B) The H4R3me2s mark may function as a docking site for the PHD finger of the de novo DNA methyltransferase DNMT3A, thereby linking PRMT5 activity to stable and heritable DNA methylation. (C) The activation marks deposed by PRMT1 (H4R3me2a) and CARM1 (H3R17me2a) can be “read” by the tudor domain of TDRD3. TDRD3 itself functions as a coactivator, in some manner relaying the intent of these two PRMTs.
