Fig. 1.
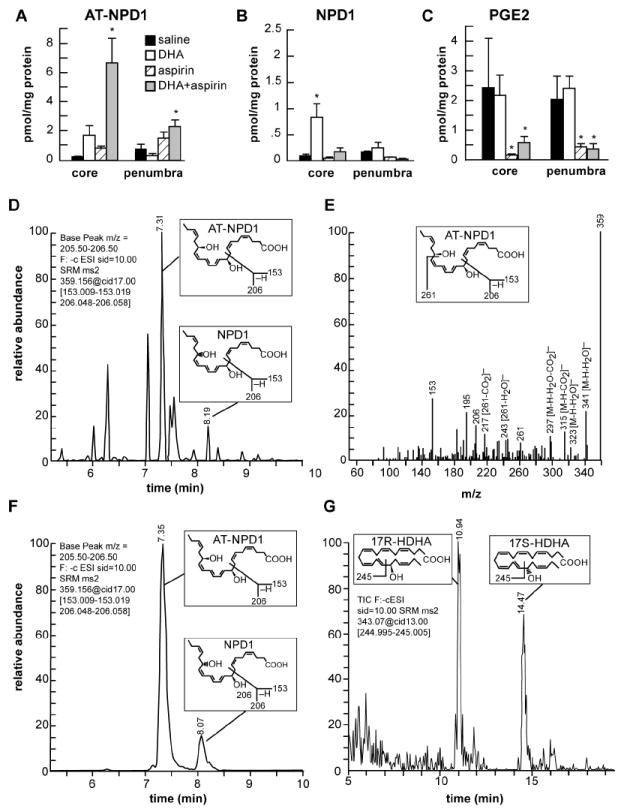
Characterization of AT-NPD1 and evidence for its biosynthesis in the ischemic brain upon systemic administration of DHA plus aspirin.
(A) AT-NPD1 synthesis was increased by DHA plus aspirin; (B) NPD1 was increased by DHA treatment; (C) PGE2 was reduced by aspirin and aspirin plus DHA treatments; (D) NPD1 and AT-NPD1, shown by a representative multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) chromatogram; (E) typical LC-MS/MS spectrum of endogenous AT-NPD1; (F) NPD1 and AT-NPD1 authentic synthetic standards shown by a MRM chromatogram; (G) 17R-HDHA and 17S-HDHA, stable derivatives of the short lived hydroperoxy precursors of AT-NPD1 and NPD1, respectively, are depicted by a representative selective reaction monitoring (SRM) chromatogram. The structure and mechanism for the generation of diagnostic mass spectrometric fragment ion for each compound are illustrated as the insert in each panel.
