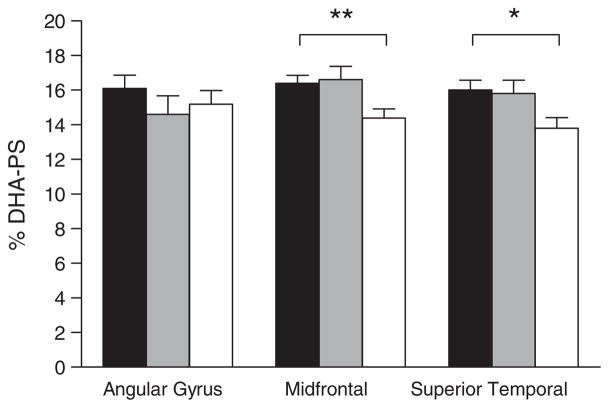
Fig. 2.
Percent composition of docosahexaenoic acid in brain phos-phatidylserine (% DHA-PS) in three brain regions in persons with no cognitive impairment. Bars are for no cognitive impairment (■, n = 12), mild cognitive impairment (
 , n = 12), or Alzheimer’s disease (□, n = 12). Data for Alzheimer’s disease were significantly different from both no cognitive impairment and mild cognitive impairment groups in the midfrontal cortex (**p = 0.014; Kruskal-Wallis followed by Mann Whitney tests) and in the superior temporal cortex (*p = 0.03; Kruskal-Wallis test). No other differences in fatty acid composition for these brain regions were observed across the three groups, or across the four brain phospholipid classes studied, regardless of whether the data were expressed as concentration (mg/g) or % composition.
, n = 12), or Alzheimer’s disease (□, n = 12). Data for Alzheimer’s disease were significantly different from both no cognitive impairment and mild cognitive impairment groups in the midfrontal cortex (**p = 0.014; Kruskal-Wallis followed by Mann Whitney tests) and in the superior temporal cortex (*p = 0.03; Kruskal-Wallis test). No other differences in fatty acid composition for these brain regions were observed across the three groups, or across the four brain phospholipid classes studied, regardless of whether the data were expressed as concentration (mg/g) or % composition.