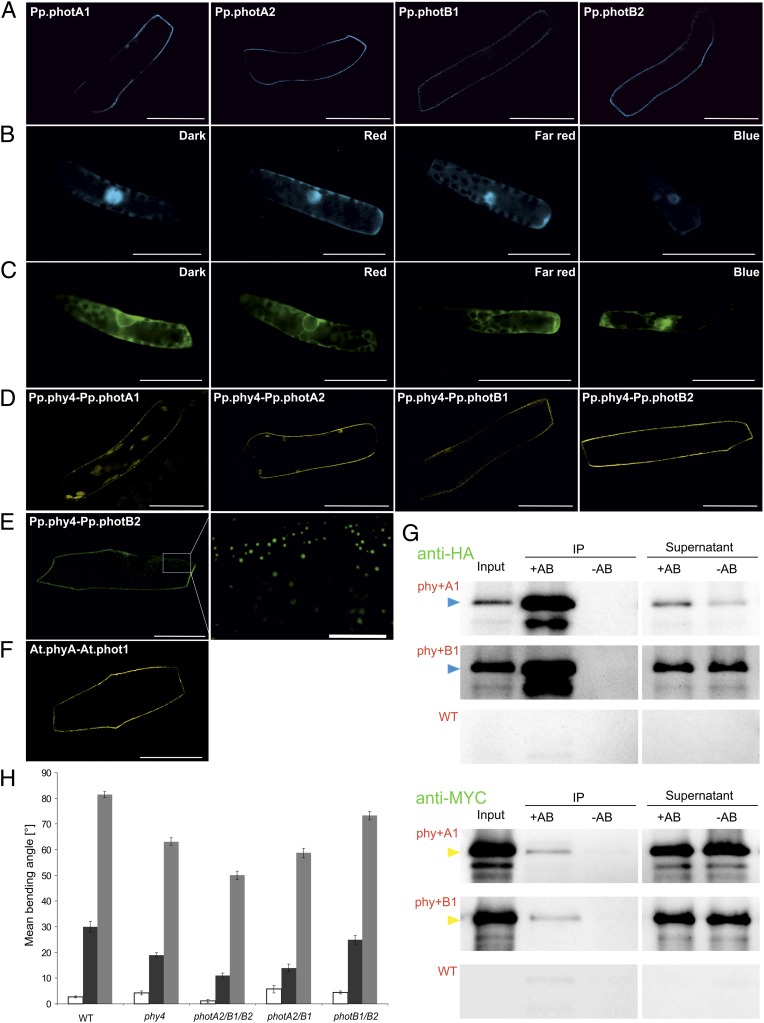
Fig. 2.
Physcomitrella phytochrome and phototropin localization and interaction in planta, phytochrome–phototropin coimmunoprecipitation, and genetic evidence for phototropin involvement in phytochrome signaling. (A–C) Localization of phototropins with CFP:Pp.phot constructs (A) and of Pp.phy4 with Pp.phy4:CFP (B) and GFP:Pp.phy4 (C) in Physcomitrella following different light pretreatments. Split-YFP showing interaction of Pp.phy4 with phototropins at the plasma membrane in Physcomitrella filament cells after 15 min R (D) and in onion epidermis cells (E, right at high magnification; scale bar: 10 μm) showing YFPC:Pp.phy4 with YFPN:Pp.photB2 interaction in discrete peripheral areas. Arabidopsis phytochrome A–phototropin 1 interaction at the plasma membrane in onion epidermal cells revealed by split-YPF after 15-min R pretreatment (F, YFPN:At.phot1 with YFPC:At.phyA). (Scale bars: 50 μm.) Anti-HA antibody immunoprecipitation (IP) of HA:Pp.phy4 with MYC:Pp.photA1 or B1 following Agrobacterium-mediated coexpression in Nicotiana benthamiana (G), detected with anti-HA (Upper, HA:Pp.phy4 as blue arrows) and anti-MYC (Lower, MYC:Pp.photA1 or B1 as yellow arrows). Negative controls were simulated IPs without anti-HA (-AB) and extracts from untransformed leaves (WT). All procedures carried out in white light (plant growth and protein extraction) or R (IP). Pp.phy4-mediated steering of directional growth in Physcomitrella wild type and phy4− or multiple phot− knockout filament tip cells (H). R-induced phototropism (dark gray) and polarotropism (light gray). Equivalent phototropism experiments with B induced no significant bending (white). SEs are shown.