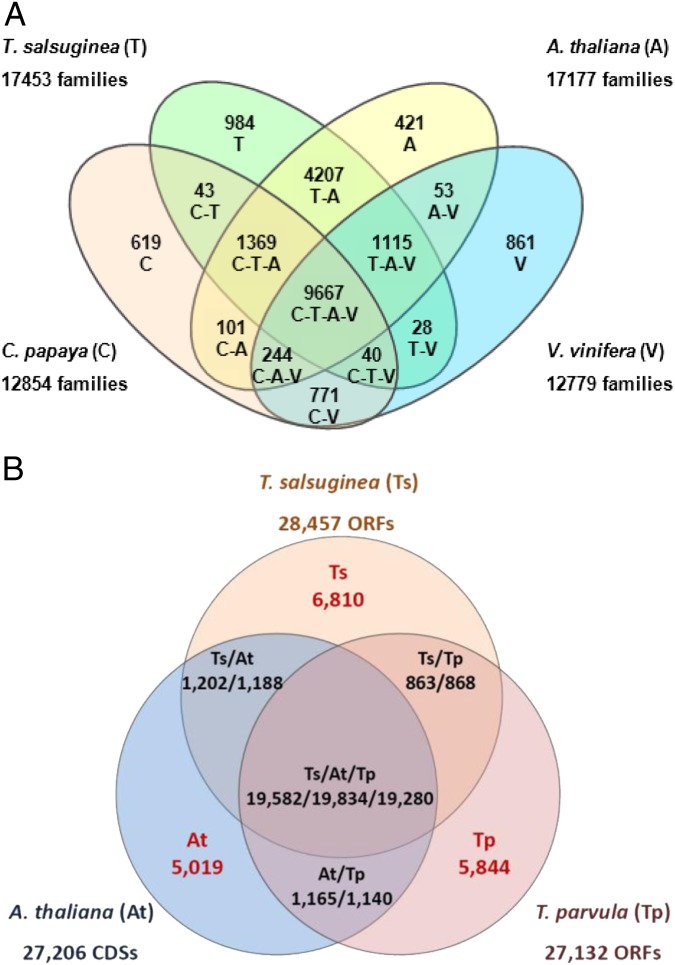
Fig. 2.
Comparison of orthologous genes and gene groups. (A) Shared orthologous gene clusters among the T. salsuginea, A. thaliana, C. papaya, and V. vinifera genomes. Program OrthoMCL was applied to identify orthologous groups among the T. salsuginea (T), A. thaliana (A), C. papaya (C), and V. vinifera (V) genomes. (B) Shared orthologous genes among crucifers T. salsuginea (Ts), T. parvula (Tp), and A. thaliana (At). Orthologs were identified using OrthoMCL. Genes from different species were considered as orthologs if the shared homology in their deduced amino acid sequences (BlastP, e < 0.00001) was more than 50% of the size of the genes being compared. Numbers of orphan genes lacking an ortholog in the other two species are shown in red. Lists of genes and their GO annotations in each category are given in Dataset S2.