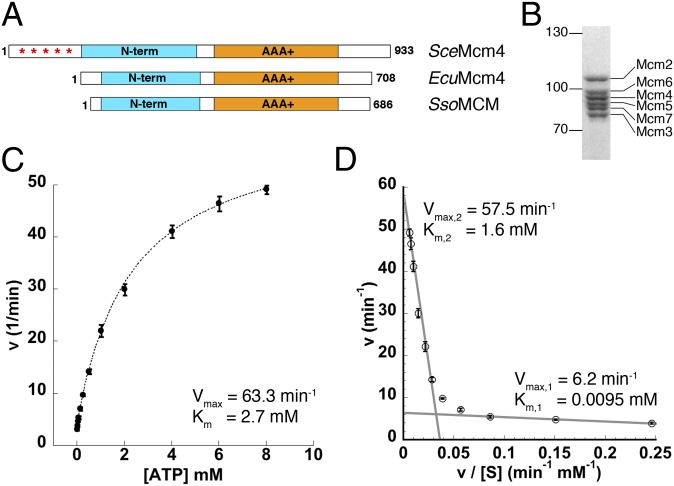
Fig. 1.
Purified EcuMCM2–7 is an active ATPase. (A) Schematic of the primary structure of (Middle) EcuMcm4 compared with (Top) SceMcm4 and (Bottom) Sulfolobus solfataricus MCM (SsoMCM). Asterisks denote the hyperphosphorylated N-terminal tail of SceMcm4. (B) Coomassie blue-stained SDS/PAGE of purified EcuMCM2–7. (C) Initial ATP hydrolysis kinetics for EcuMCM2–7 plotted as a function of ATP concentration. (D) Eadie–Hofstee plot of EcuMCM2–7 ATPase activity. Linear regions of low- and high-velocity turnover are indicated by gray lines.