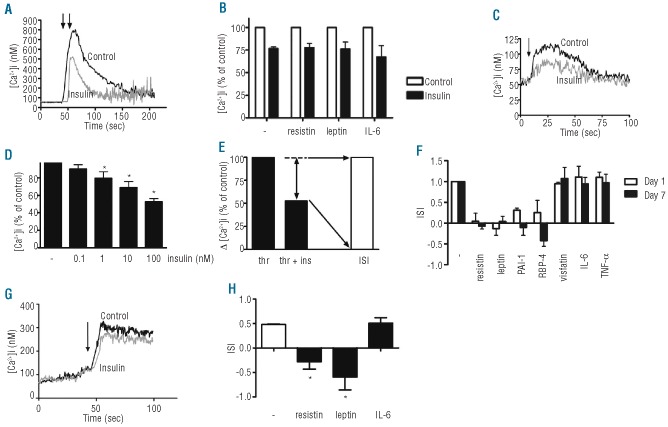
Figure 1.
Resistin, leptin, PAI-1 and RBP4 induce insulin resistance in CHRF-288-11 cells. (A,B) Inhibition by insulin of thrombin-induced Ca2+ mobilization ([Ca2+]i,) in platelets is unaffected by adipokines. Thrombin (1 U/mL)-induced Ca2+ mobilization in platelets pre-incubated without and with insulin (100 nM, 5 min, 37°C) in the presence (2 h, 37°C) of resistin (150 ng/mL), leptin (300 ng/mL) and IL-6 (12 ng/mL). (C,D) Inhibition by insulin of thrombin induced Ca2+ mobilization in CHRF-288-11 cells. Thrombin (1 U/mL)--induced Ca2+ mobilization in CHRF-288-11 cells pre-incubated without and with indicated insulin concentrations (f.c.; 5 min, 37°C). (E) Insulin inhibition was expressed as an insulin sensitivity index, ISI. (F) Resistin, leptin, PAI-1 and RBP4 induce insulin-resistance, but visfatin, IL-6 and TNF-αdo not. Inhibition of Ca 2+ mobilization by insulin (100 nM) in CHRF-288-11 cells after 1 and 7 days culture in the presence of resistin (150 ng/mL), leptin (300 ng/mL), PAI-1 (260 ng/mL), RBP4 (500 ng/mL), visfatin (20 ng/mL), IL-6 (12 ng/mL) and TNF-α(50 pg/mL). These concentrations were used in all experiments, unless indicated otherwise. (G) Thrombin (1 U/mL)-induced Ca2+ mobilization in primary megakaryocytes pre-incubated without and with insulin (100 nM, 5 min, 37°C) in the absence of adipokines. (H) Resistin and leptin, but not IL-6 completely reduced insulin sensitivity in primary megakaryocytes. Cells were incubated with vehicle, resistin, leptin and IL-6 (1 day, 37°C) and insulin inhibition of Ca2+ mobilization was measured. An ISI=1.0 refers to insulin inhibition in the absence of adipokines. (data are means ± SEM, n=3 and were analyzed with Student’s test, *denotes a statistically significant difference, P<0.05).