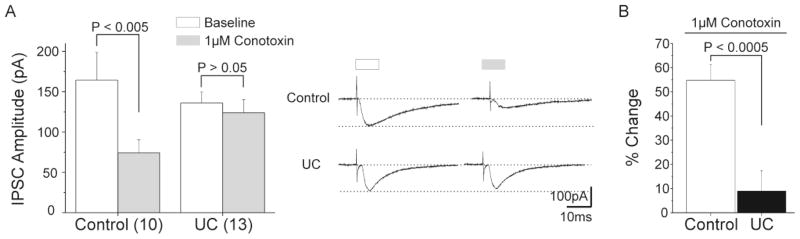
Figure 2. Effects of N-type channel blockade in layer V inhibitory terminals of control and UC cortex.
A. Baseline mean peak amplitude of control eIPSCs decreased by approximately 50% after local perfusion of 1 μM ω-conotoxin GVIA (left). In contrast, no difference was observed in baseline peak amplitude of eIPSCs after treatment in UCs (right). Inset: Representative traces of eIPSCs recorded in control (upper traces) and UC (lower traces) layer V Pyr cells at baseline (white bar) and after 1 μM ω-conotoxin GVIA (gray bar).
B. Normalized changes in baseline peak amplitude of eIPSCs after N-channel blockade in layer V Pyr cells from control and UC. Change in peak amplitude of eIPSC after N-channel blockade is significantly greater in control than in UCs.