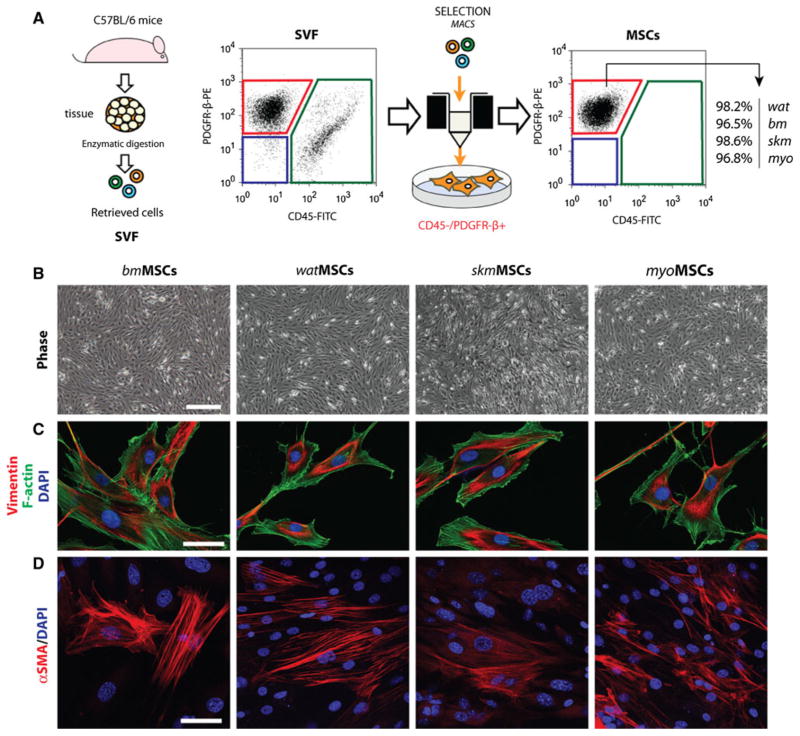
Fig. 1.
Isolation and characterization of MSCs from four different murine tissues. a Tissue-resident MSCs were isolated from the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of four different murine tissues: white adipose tissue (wat), bone marrow (bm), skeletal muscle (skm), myocardium (myo). MSCs were selected based on their negative expression of CD45 and positive expression of PDGFR-β using magnetic activated cell sorting (MACS). b Phase-contrast micrographs of confluent MSCs after 3 passages in culture (scale bar 100 μm). c Indirect immunofluorescent staining of MSCs using an anti-vimentin antibody. Cells were counterstained with phalloidin for F-actin filaments and DAPI for nuclei (scale bar 20 μm) d Immunofluorescent staining of MSCs using an anti-α-SMA antibody and DAPI (scale bar 20 μm)