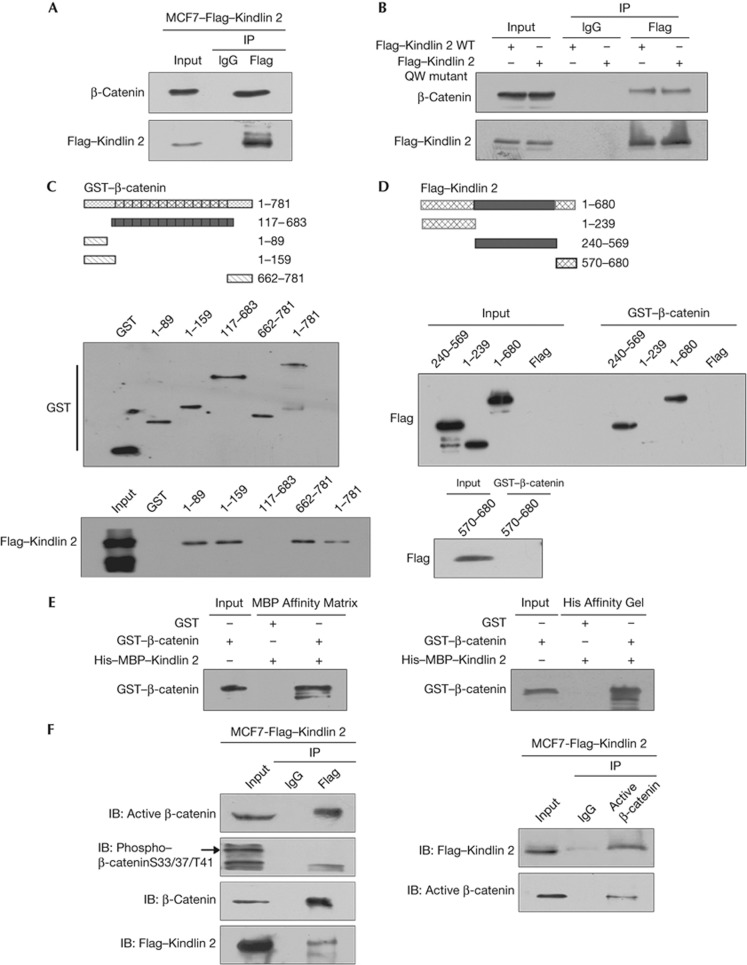
Figure 1.
Kindlin 2 directly interacts with β-catenin. (A) Cell lysates were prepared and Flag antibody was then used in co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP), followed by western blot (WB) analysis using indicated antibodies. (B) A Flag–Kindlin 2 QW mutant deficient in binding to integrin β1 was generated. Both the wild-type (WT) and mutant Flag–Kindlin 2 were transfected into 293T cells, protein was then extracted for Co-IP. (C) Glutathione S-transferase (GST)-fusion proteins for different regions of β-catenin were designed as in the upper panel. Purified GST or GST–β-catenin fragments were evaluated by WB (middle). Different fusion proteins were incubated with total lysates of MCF7–Flag–Kindlin 2 stable cells for GST-pulldown assay, followed by WB (bottom). (D) Different fragments of Flag–Kindlin 2 were listed as in the upper panel. The Kindlin 2 fragments were expressed in 293T cells and evaluated by WB (input). GST-pulldown assays were performed by incubating the GST–β-catenin with the Kindlin 2 fragments. (E) Fusion protein His–MBP–Kindlin 2 was incubated with GST or GST–β-catenin in vitro for His/MBP-pulldown assays. Affinity matrices for MBP or His-tags were used separately. (F) Lysates from MCF7–Flag–Kindlin 2 were extracted, and then Flag or active β-catenin antibodies were used for Co-IP, followed by WB. IB, immunoblot; IgG, immunoglobin-G.