Figure 1.
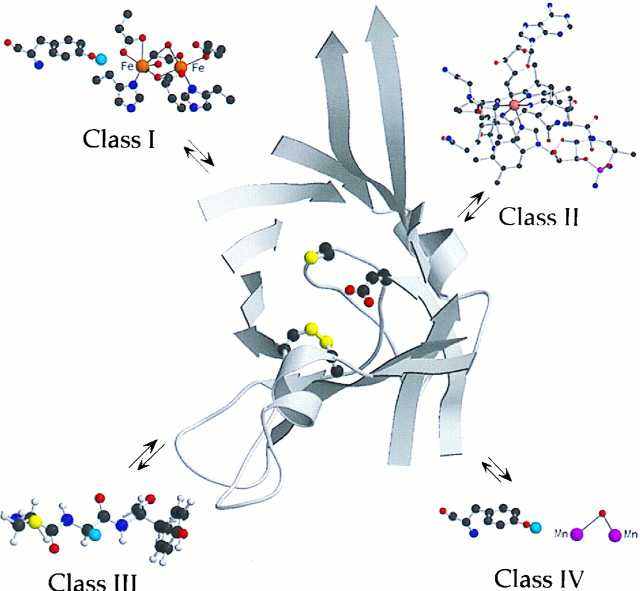
The active site of the Escherichia coli R1 subunit, adapted from Uhlin and Eklund (4). Cys-439, the site of the putative thiyl radical, is at the tip of the central loop of the barrel with Glu-441, the conserved glutamate adjacent to this residue. In addition, a disulfide is shown between Cys-225 and Cys-419, the site of delivery of the reducing equivalents to make deoxynucleotide. Each class of RNR thus far characterized has a different cofactor: the class I RNR has a diferric–tyrosyl radical (blue balls represent the orbital with the unpaired electron); class II utilizes AdoCbl; class III utilizes S-adenosylmethionine and an iron–sulfur cluster to generate a glycyl radical; and class IV is proposed to have a Mn cofactor adjacent to a tyrosyl radical. The cofactors’ function is proposed to be the generation of the thiyl radical, which will be located, regardless of the class of RNR, in an active site with secondary and tertiary structure similar to that observed in class I R1. The figure was generated by using molscript (34) and raster3d (35).
