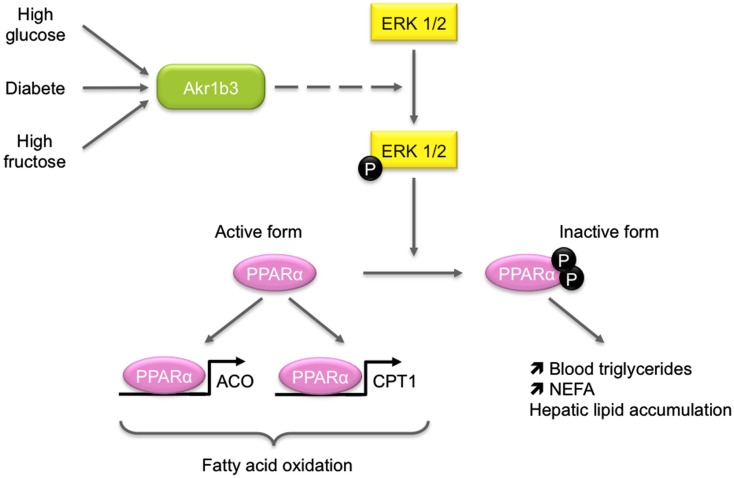
Figure 6.
Role of Akr1b3 in hepatic lipid homeostasis. Diabetic conditions (high glucose or high fructose) lead to Akr1b3 up-regulation and Akr1b3-dependent ERK1/2 activation and are often associated to dyslipidemia. The ERK1/2 mediated phosphorylation of PPARγ inhibits its transcriptional activity resulting in down-regulation of β-oxidation master genes. Impaired β-oxidation favors hepatic lipid accumulation and increases blood triglycerides and non-esterified fatty acids (NEFA). The mechanism by which Akr1b3 induces ERK1/2 phosphorylation is still unknown (dashed lines).