Abstract
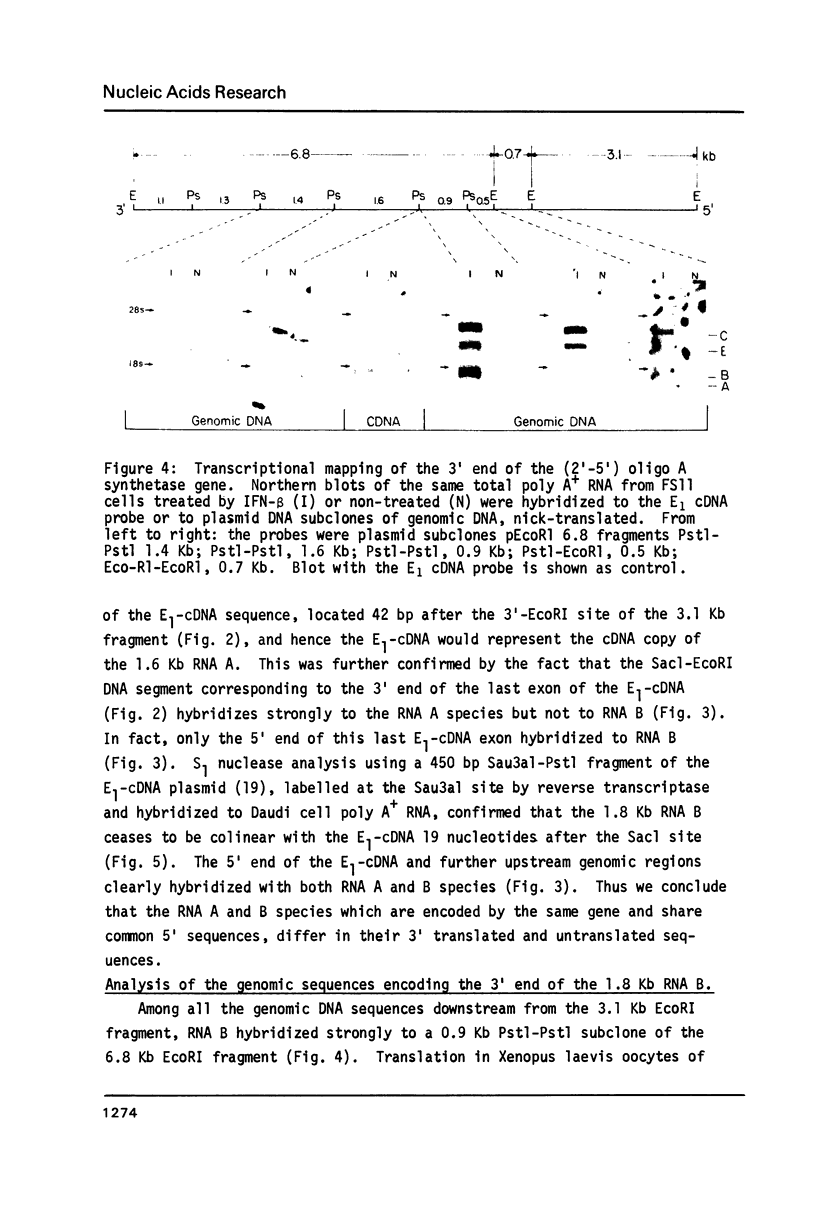
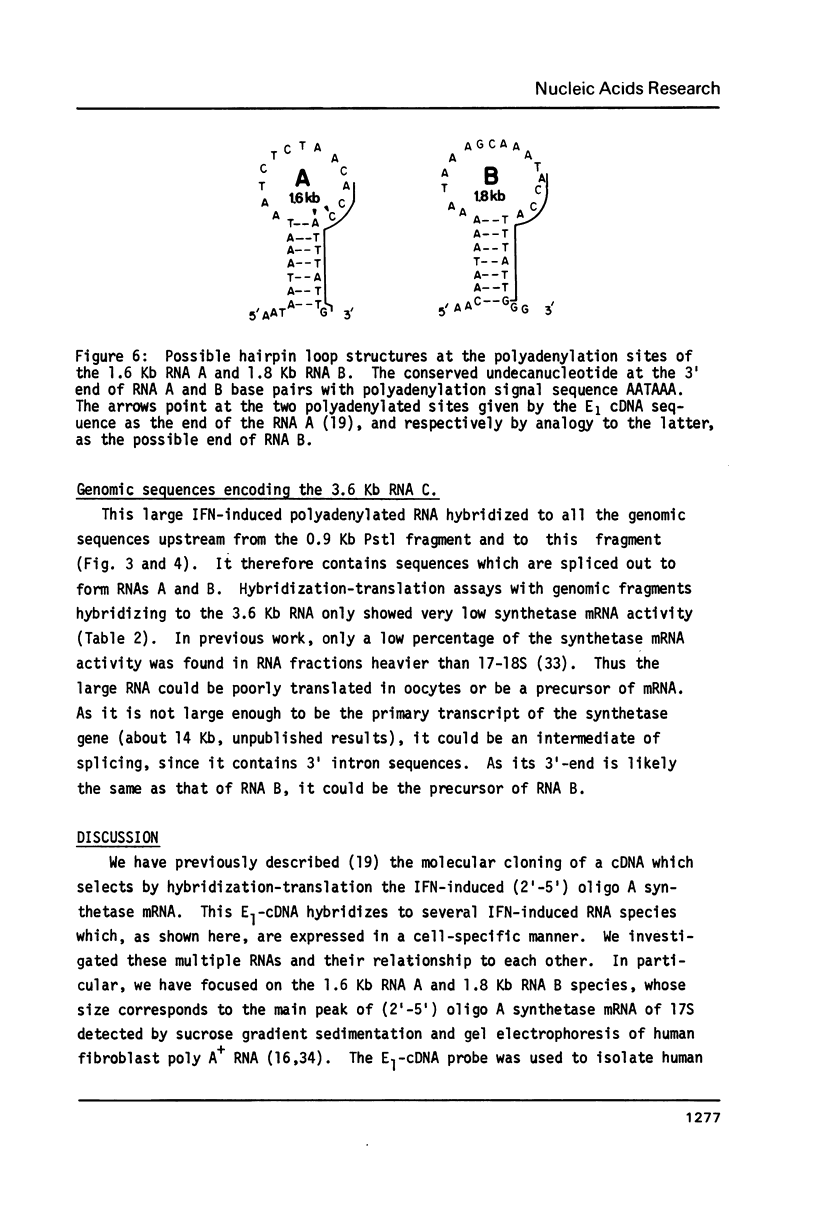
Analysis of the sizes of the (2'-5') oligo A synthetase polyadenylated transcripts in various human cell lines by hybridization with a cDNA probe revealed that the pattern of the transcripts was cell-type specific. In order to investigate whether the 1.6 Kb, 1.8 Kb and 3.6 Kb mRNA, which are predominantly expressed in different cell-lines, encode different proteins or could differ in the size of their 3' or 5' untranslated sequences, the corresponding gene was isolated. On Southern blots of human genomic RNA, the cDNA probe hybridize to a 3.1 Kb EcoRI fragment. Three overlapping genomic clones were isolated which contain the same 3.1 Kb EcoRI fragment. Transcriptional mapping of the 3' end of the gene by Northern blots, hybridization translation experiments and sequencing showed that the 1.6 and 1.8 Kb mRNA are produced by a differential processing at the 3' end of the primary transcript of the same gene. The polyadenylation site of the 1.6 Kb mRNA is located 1.9 Kb upstream to the one of the 1.8 Kb mRNA. To produce the latter transcript, a portion of the last exon of the 1.6 Kb mRNA (including a segment coding for a very hydrophobic sequence of 18 amino acids and 3' untranslated sequence) is spliced out. The two mRNAs thus encode two different proteins which could have different affinity for cellular elements. The 3.6 Kb transcript has the same polyadenylation site as the 1.8 Kb mRNA, but contains additional unspliced 3' intron sequences.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chebath J., Merlin G., Metz R., Benech P., Revel M. Interferon-induced 56,000 Mr protein and its mRNA in human cells: molecular cloning and partial sequence of the cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1213–1226. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernajovsky Y., Kimchi A., Schmidt A., Zilberstein A., Revel M. Differential effects of two interferon-induced translational inhibitors on initiation of protein synthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1979 May 2;96(1):35–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13010.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty J. P., Samanta H., Farrell P. J., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA, and RNA degradation. Isolation of homogeneous pppA(2'p5'A)n-1 synthetase from Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3813–3816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Rogers J., Davis M., Calame K., Bond M., Wall R., Hood L. Two mRNAs can be produced from a single immunoglobulin mu gene by alternative RNA processing pathways. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90617-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellous M., Nir U., Wallach D., Merlin G., Rubinstein M., Revel M. Interferon-dependent induction of mRNA for the major histocompatibility antigens in human fibroblasts and lymphoblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3082–3086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Brown R. E. pppA2'p5'A2'p5'A: an inhibitor of protein synthesis synthesized with an enzyme fraction from interferon-treated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):256–260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimchi A., Shure H., Revel M. Anti-mitogenic function of interferon-induced (2'-5')oligo(adenylate) and growth-related variations in enzymes that synthesize and degrade this oligonucleotide. Eur J Biochem. 1981;114(1):5–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimchi A., Shure H., Revel M. Regulation of lymphocyte mitogenesis by (2'--5') oligo-isoadenylate. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):849–851. doi: 10.1038/282849a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr, Fahey D. Human fibroblast interferon. An improved purification. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3609–3611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Biochemistry of interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:251–282. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt M. A., Imperiale M. J., Ali H., Nevins J. R. Requirement of a downstream sequence for generation of a poly(A) addition site. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):993–999. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90433-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlin G., Chebath J., Benech P., Metz R., Revel M. Molecular cloning and sequence of partial cDNA for interferon-induced (2'-5')oligo(A) synthetase mRNA from human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4904–4908. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minks M. A., West D. K., Benvin S., Baglioni C. Structural requirements of double-stranded RNA for the activation of 2',5'-oligo(A) polymerase and protein kinase of interferon-treated HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10180–10183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mory Y., Chernajovsky Y., Feinstein S. I., Chen L., Nir U., Weissenbach J., Malpiece Y., Tiollais P., Marks D., Ladner M. Synthesis of human interferon beta 1 in Escherichia coli infected by a lambda phage recombinant containing a human genomic fragment. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(1):197–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. The pathway of eukaryotic mRNA formation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:441–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K., Vuocolo G. A. Synthesis of two mRNAs by utilization of alternate polyadenylation sites: expression of SV40-mouse immunoglobulin mu chain gene recombinants in Cos monkey cells. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):689–699. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01871.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick D., Eshhar Z., Fischer D. G., Friedlander J., Rubinstein M. Monoclonal antibodies to human interferon-gamma: production, affinity purification and radioimmunoassay. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1527–1530. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01618.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick D., Eshhar Z., Rubinstein M. Monoclonal antibodies to human alpha-interferon and their use for affinity chromatography. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2244–2247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revel M. F., Kimchi A. Initial characterization of a spontaneous interferon secreted during growth and differentiation of Friend erythroleukemia cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1472–1480. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revel M., Kimchi A., Friedman M., Wolf D., Merlin G., Panet A., Rapoport S., Lapidot Y. Cell-regulatory functions of interferon induced enzymes: antimitogenic effect of (2'-5')oligo-A, growth-related variations in (2'-5')oligo-A synthetase, and isolation of its mRNA. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1981;41:452–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revel M., Wallach D., Merlin G., Schattner A., Schmidt A., Wolf D., Shulman L., Kimchi A. Interferon-induced enzymes: microassays and their applications: purification and assay of (2'-5')-oligoadenylate synthetase and assay of 2'-phosphodiesterase. Methods Enzymol. 1981;79(Pt B):149–161. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)79024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa F., Fellous M., Dron M., Tovey M., Revel M. Presence of an abnormal beta 2-microglobulin mRNA in Daudi cells: induction by interferon. Immunogenetics. 1983;17(2):125–131. doi: 10.1007/BF00364752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. G., Mermod J. J., Amara S. G., Swanson L. W., Sawchenko P. E., Rivier J., Vale W. W., Evans R. M. Production of a novel neuropeptide encoded by the calcitonin gene via tissue-specific RNA processing. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):129–135. doi: 10.1038/304129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Zilberstein A., Shulman L., Federman P., Berissi H., Revel M. Interferon action: isolation of nuclease F, a translation inhibitor activated by interferon-induced (2'-5') oligo-isoadenylate. FEBS Lett. 1978 Nov 15;95(2):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smekens-Etienne M., Goldstein J., Ooms H. A., Dumont J. E. Variation of (2'-5')oligo(adenylate) synthetase activity during rat-liver regeneration. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Feb 1;130(2):269–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07146.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Laurent G., Yoshie O., Floyd-Smith G., Samanta H., Sehgal P. B., Lengyel P. Interferon action: two (2'-5')(A)n synthetases specified by distinct mRNAs in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells treated with interferon. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):95–102. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90338-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Zeevi M., Landau T., Revel M. Identification of the translation products of human fibroblast interferon mRNA in reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;98(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13153.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. R., Golgher R. R., Brown R. E., Gilbert C. S., Kerr I. M. Natural occurrence of 2-5A in interferon-treated EMC virus-infected L cells. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):582–586. doi: 10.1038/282582a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. R., Kerr I. M. Inhibition of protein synthesis by 2'-5' linked adenine oligonucleotides in intact cells. Nature. 1978 Nov 2;276(5683):88–90. doi: 10.1038/276088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang K., Samanta H., Dougherty J., Jayaram B., Broeze R., Lengyel P. Interferons, double-stranded RNA, and RNA degradation. Isolation and characterization of homogeneous human (2'-5')(a)n synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9324–9328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden A., Shure-Gottlieb H., Chebath J., Revel M., Kimchi A. Autogenous production of interferon-beta switches on HLA genes during differentiation of histiocytic lymphoma U937 cells. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):969–973. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01915.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





