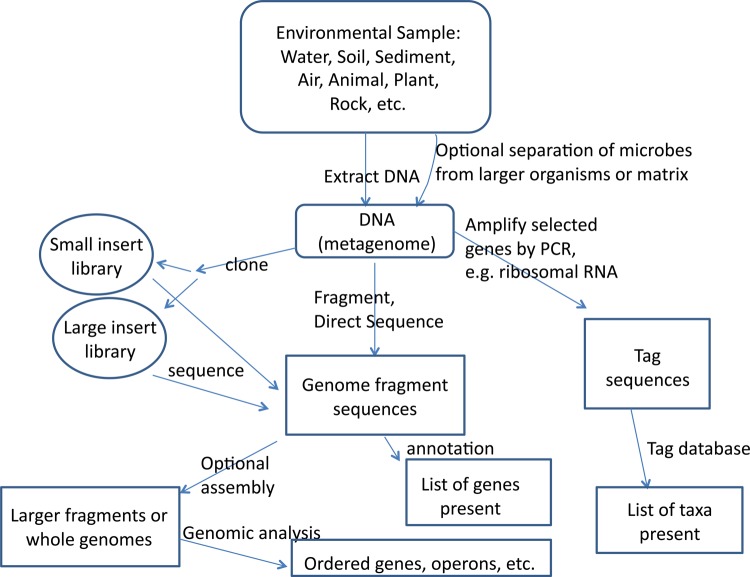
Figure 1. Schematic of shotgun and targeted metagenomic analysis.
The metagenome is the collective genomic DNA of organisms (usually microorganisms) in a given sample. After sampling, and sometimes attempts to separate microorganisms from larger organisms, DNA is extracted from the total biomass. For overall genomic analysis, older studies cloned various size fragments and sequenced them. Next generation sequencing shotgun sequencing studies now generally fragment the DNA and sequence the fragments directly, assembling some of them into overlapping ‘contigs’, larger ‘scaffolds’, or even whole genomes. In contrast, tag sequencing uses polymerase chain reaction to amplify specific genes of interest, most often 16S rRNA, and the amplified fragments are sequenced directly.