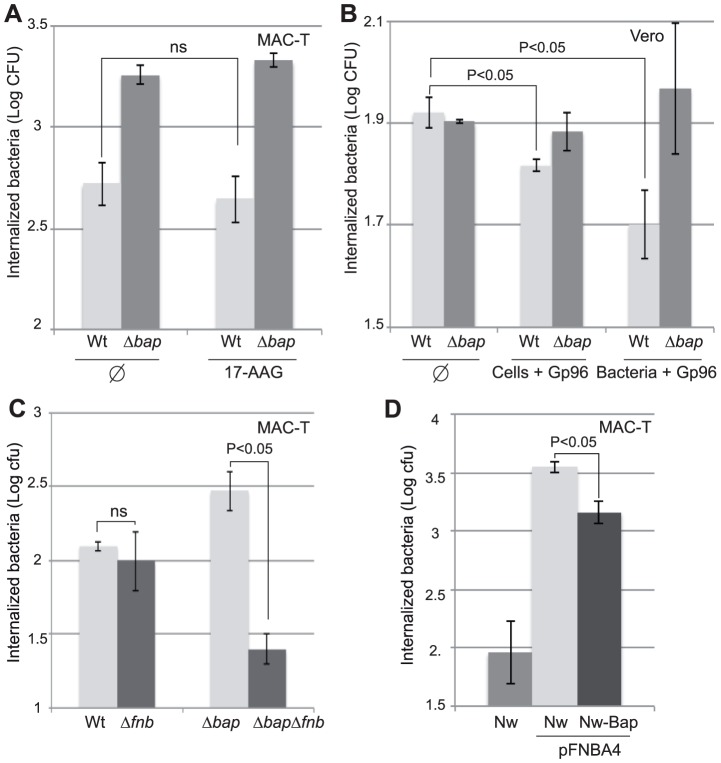
Figure 7. The expression of Bap minimized S. aureus cell entry by interfering with the FnBPs.
A) Evaluation of the effect of 17-AAG on the invasion phenotype mediated by Bap. MAC-T cells were treated overnight with 1 µmol/l of 17-AAG, an inhibitor of HSP90. Invasion assays were then carried out with either S. aureus V329 and Δbap strain. Internalized bacteria were determined by CFU count after gentamicin assay. B) Transcomplementation of Vero cells with Gp96. Invasion assay with S. aureus V329 and Δbap was performed in Vero cells (φ), in Vero cells incubated with 10 µg/ml of recombinant Gp96 for 30 min before infection (Cells+Gp96) or with bacteria pre-incubated with 5 µg/ml of recombinant Gp96 (Bacteria+Gp96). C)Inhibition of bacterial invasion mediated by Bap requires the FnBPs. Invasion of S. aureus V329 wild type (Wt), a mutant in FnBPs (Δfnb), Δbap and double mutant ΔfnbΔbap. After 1 h infection invasion values were calculated as the number of bacteria that survived to 2 h of gentamicin treatment in MAC-T cells.(D) MAC-T cells invasion with S. aureus Newman (Nw) and Newman_Bap complemented with plasmid pFNBA4 that expresses the fnbA gene. Experiments were performed in triplicate and repeated three times.