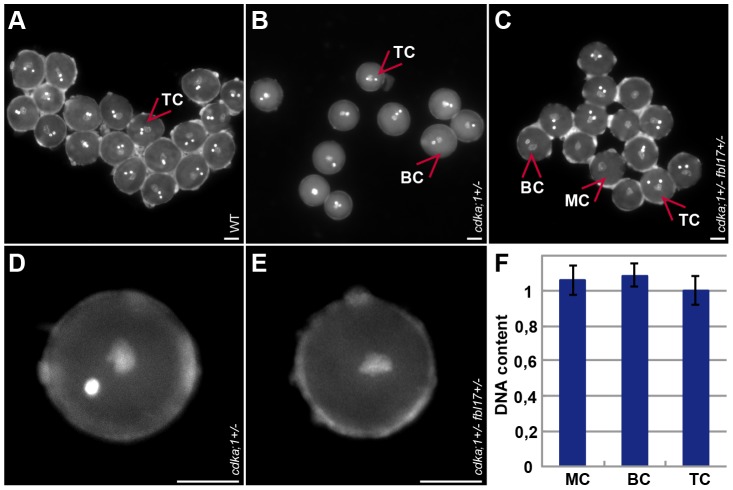
Figure 1. Pollen phenotypes of mutants for components of the G1/S phase control module.
(A) Tricellular mature wild-type DAPI-stained pollen at anthesis (one vegetative cell enclosing two sperm cells). (B) DAPI-stained pollen at anthesis from heterozygous cdka;1 mutant plants (similar to pollen from heterozygous fbl17 mutants, data not shown) containing approximately 43% bicellular pollen (one vegetative cell and one sperm-cell-like cell) and 57% tricellular, wild-type-like pollen. (C) DAPI-stained pollen at anthesis from double heterozygous cdka;1 fbl17 mutant plants carrying a hemizygous ProCDKA;1:CDKA;1:YFP rescue construct (similar to pollen from e2fa−/− fbl17+/− mutants, data not shown) and containing single-celled pollen grains (only one vegetative-like cell), in addition to bicellular (cdka;1/fbl17-like) and tricellular (wild-type-like) pollen. (D) Close-up of bicellular pollen as found in cdka;1 or fbl17 heterozygous plants. (E) Close-up of monocellular pollen grains as found in cdka;1 fbl17 or e2fa fbl17 double heterozygous mutants. (F) Quantification of DAPI-stained pollen. The DNA content of the single-celled pollen from cdka;1+/− fbl17+/− or e2fa−/− fbl17+/− double mutants reaches 1C, similarly to the vegetative nucleus in wild-type pollen and, thus, resides in a G1 phase.