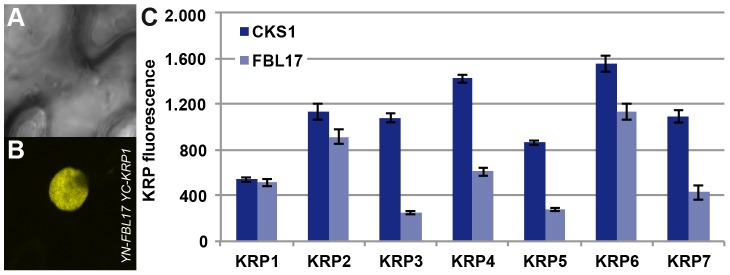
Figure 4. Interaction of FBL17 with KRPs in BiFC assays and degradation promotion of KRP in vivo.
Two nonfluorescent fragments (YN and YC) of the yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) fused to FBL17 (YN-FBL17) and seven different CDK inhibitors (YC-KRP1–7). Co-production of FBL17 and KRP1-KRP7 fusions in tobacco leaves reconstituted the expected yellow fluorescence for all seven protein combinations. Exemplarily, one interaction in the BiFC assays is shown in (A–B) displaying the interaction of FBL17 with KRP1 under bright field (A) and epifluorescence (B). (C) Transient expression assays were conducted in tobacco leaves to determine whether FBL17 can target CDK inhibitors for degradation. Among the seven KRPs, FBL17 can especially reduce the fluorescence, implying protein degradation, for KRP3, KRP4, KRP5 and KRP7, whereas the fluorescence intensity of KRP2 and KRP6 diminished only moderately after co-infiltration with FBL17. CKS1 was used as a reference.