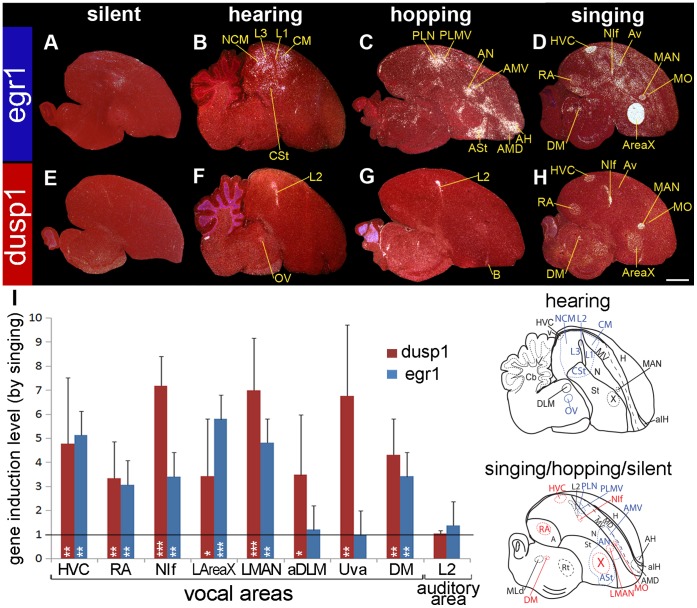
Figure 2. Egr1 and dusp1 mRNA expression in zebra finch brain induced by hearing, hopping, and singing.
(A–D) Darkfield images of in situ hybridizations with egr1 from male zebra finches of four different behavioral conditions: (A) silent control sitting in the dark; (B) sitting and hearing song for 30 min in the dark; (C) deaf animals hopping in a rotating wheel in the dark; and (D) singing alone (>305.6 sec; >102 song bouts) and some hopping for 30 min in the light. (E–H) Adjacent sagittal sections hybridized to dusp1. All animals were in sound attenuation chambers. Three regions show overlap of hearing-driven and movement-driven gene expression: egr1 in PLN and PLMV, and dusp1 in the adjacent part of L2. See [29], [34] for more details on hearing- and movement-driven gene expression results. Song nuclei are the only areas with overlap in induced high levels of egr1 and dusp1 expression. The anatomical drawings below the image show brain regions activated by hearing (medial brain section) or other conditions (lateral brain section), with vocal areas highlighted in red. White, gene expression, mRNA signal. Red, cresyl violet stain. Sections are sagittal. Scale bar = 2 mm. (I) Quantification of dusp1 and egr1 expression. Values significantly above 1 indicate induced expression in singing animals (n = 4, except for DLM and Uva n = 3) relative to average of silent controls (n = 3). Birds that sang >83.0 sec (>34 song bouts) in 30 min were used. The standard deviations of expression were large due to differences in singing amount (see Fig. 4A). Overall differences were significant (p<0.001, repeated measure ANOVA between singing and silent groups). * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, and *** p<0.001, unpaired t-test in each nucleus relative to silent control. Error bars, ±SD. The highest to lowest levels for dusp1 were in NIf, LMAN, Uva > HVC > DM, DLM, X, RA (p<0.01, ANOVA); For egr1 - AreaX > HVC > LMAN > NIf > RA > Uva, DLM (p<0.05, ANOVA). Abbreviations: A, Arcopallium; aIH, anterior part of the intercalated layer of the hyperpallium; H, hyperpallium; Hp, hippocampus; M, mesopallium; MD, dorsal mesopallium; MV, ventral mesopallium; N, nidopallium; Rt, nucleus rotundus; St, striatum; v, ventricle. For other anatomical abbreviations, see Table 1.