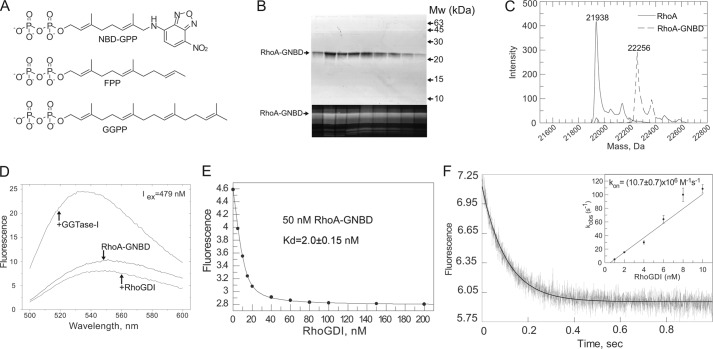
FIGURE 3.
Construction and analysis of prenylated fluorescent RhoA sensor. A, chemical structure of NBD-GPP in comparison with structures of FPP and GGPP. B, SDS-PAGE analysis of RhoA-GNBD eluted from Superdex 200 size exclusion column. The upper panel shows a gel stained with Coomassie Blue, whereas the lower panel shows a fluorescent scan of the same gel (excitation laser, 473 nm; cutoff filter, 510 nm). C, ESI-MS analysis of RhoA-GNBD. D, emission spectra of 50 nm solution of RhoA-GNBD before or after addition of 1 μm RhoGDI or GGTase-I. E, titration of RhoGDI to 50 nm solution of RhoA-GNBD. The fluorescence of the NBD group was excited at 479 nm, and the emission was collected at 560 nm. The Kd value of 2 nm was calculated by fitting data to the quadratic equation using Grafit 5.0. F, kinetic analysis of RhoGDI interaction with the RhoA-GNBD. The graph represents a typical time course of fluorescence signal changes upon rapid mixing of 100 nm RhoA-GNBD and 1.5 μm RhoGDI at 25 °C. The solid curve shows the single-exponential fit to the data. The inset represents a plot of the observed pseudo-first order rate constant kobs versus concentration of RhoGDI.