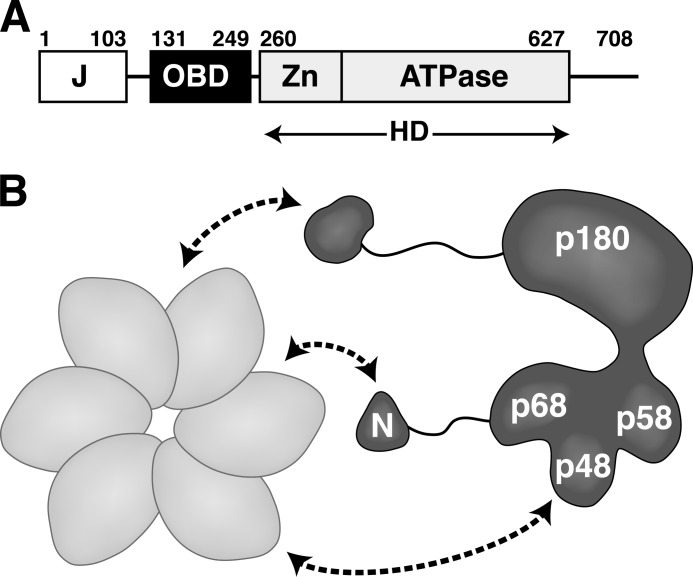
FIGURE 1.
Schematic diagram of the interactions of hexameric LTag with Pol-prim. A, modular architecture of SV40 LTag (27, 51). Each of the three structured domains is sufficient for its biochemical activity as follows: DnaJ chaperone domain (J), origin DNA binding domain (OBD), and helicase domain (HD), composed of the zinc (Zn) and ATPase subdomains, are boxed. Flexible linker regions are indicated as lines. B, hexameric helicase domain of LTag (light gray) contacts Pol-prim (dark gray) through at least three subunits (curved arrows). The N-terminal regions (N) of p180 and p68 are dispensable for enzymatic activity but interact physically with LTag (9, 17, 23, 60).