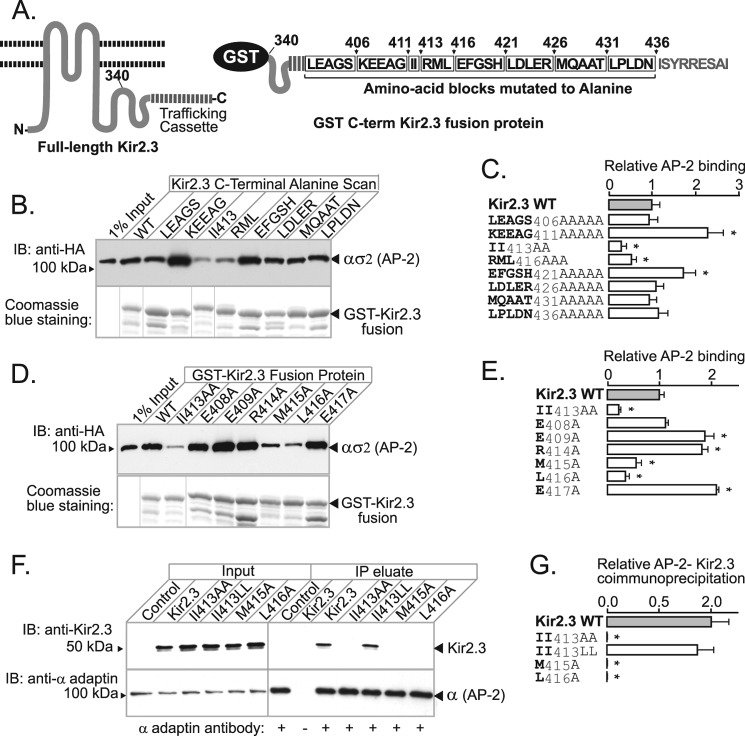
FIGURE 4.
Hydrophobic residues in Kir2.3 located downstream of di-Ile413 contribute to AP-2 binding. A, schematic representation of the C terminus of Kir2.3 expressed as a GST fusion protein (left), highlighting blocks of residues subjected to alanine scanning mutagenesis (right). B, representative binding study. Mutants are identified by residues replaced with alanine. AP-2 ασ2 bound to the WT and each of the mutant fusion proteins (lower panel) was accessed in Western blotting with anti-HA antibody (upper panel). IB, immunoblot. C, densitometric quantification and summary of the data from three separate experiments (mean ± S.E.; *, p < 0.05). D, representative binding study of point mutants. E, densitometric quantification and summary of the data from three separate experiments (mean ± S.E.; *, p < 0.05). F, identical hydrophobic residues are required for the interaction and co-immunoprecipitation of Kir2.3 expressed in HEK293 cells with endogenous AP-2. IP, immunoprecipitate. G, densitometric quantification and summary of the data from three separate experiments (mean ± S.E.; *, p < 0.05).